Localization of mRNAs coding for peroxisomal proteins in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 19903887
- PMCID: PMC2785255
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910754106
Localization of mRNAs coding for peroxisomal proteins in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
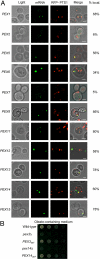
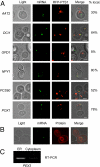
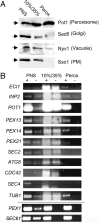
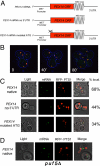
Targeted mRNA trafficking and local translation may play a significant role in controlling protein localization. Here we examined for the first time the localization of all ( approximately 50) mRNAs encoding peroxisomal proteins (mPPs) involved in peroxisome biogenesis and function. By using the bacteriophage MS2-CP RNA-binding protein (RBP) fused to multiple copies of GFP, we demonstrated that >40 endogenously expressed mPPs tagged with the MS2 aptamer form fluorescent RNA granules in vivo. The use of different RFP-tagged organellar markers revealed 3 basic patterns of mPP granule localization: to peroxisomes, to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and nonperoxisomal. Twelve mPPs (i.e., PEX1, PEX5, PEX8, PEX11-15, DCI1, NPY1, PCS60, and POX1) had a high percentage (52%-80%) of mRNA colocalization with peroxisomes. Thirteen mPPs (i.e., AAT2, PEX6, MDH3, PEX28, etc.) showed a low percentage (30%-42%) of colocalization, and 1 mPP (PEX3) preferentially localized to the ER. The mPPs of the nonperoxisomal pattern (i.e., GPD1, PCD1, PEX7) showed <<30% colocalization. mPP association with the peroxisome or ER was verified using cell fractionation and RT-PCR analysis. A model mPP, PEX14 mRNA, was found to be in close association with peroxisomes throughout the cell cycle, with its localization depending in part on the 3'-UTR, initiation of translation, and the Puf5 RBP. The different patterns of mPP localization observed suggest that multiple mechanisms involved in mRNA localization and translation may play roles in the importation of protein into peroxisomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells lacking Pex3 contain membrane vesicles that harbor a subset of peroxisomal membrane proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017 Oct;1864(10):1656-1667. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.05.021. Epub 2017 May 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28552664 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxins Pex30 and Pex29 Dynamically Associate with Reticulons to Regulate Peroxisome Biogenesis from the Endoplasmic Reticulum.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jul 22;291(30):15408-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.728154. Epub 2016 Apr 29. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27129769 Free PMC article.
-
A role for mRNA trafficking and localized translation in peroxisome biogenesis and function?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1863(5):911-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.09.007. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26367800 Review.
-
Pex3p initiates the formation of a preperoxisomal compartment from a subdomain of the endoplasmic reticulum in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 14;280(41):34933-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506208200. Epub 2005 Aug 8. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16087670
-
Targeting and insertion of peroxisomal membrane proteins: ER trafficking versus direct delivery to peroxisomes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1863(5):870-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.09.021. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26392202 Review.
Cited by
-
Localized translation near the mitochondrial outer membrane: An update.RNA Biol. 2015;12(8):801-9. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1058686. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26151724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PUF3 RNA binding protein of Trypanosoma cruzi regulates mitochondrial morphology and function.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 14;10(12):e32810. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32810. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39022037 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria as emergency landing for abandoned peroxins.EMBO Rep. 2021 Oct 5;22(10):e53790. doi: 10.15252/embr.202153790. Epub 2021 Aug 19. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 34414648 Free PMC article.
-
Acyl CoA oxidase: from its expression, structure, folding, and import to its role in human health and disease.Mol Genet Genomics. 2023 Nov;298(6):1247-1260. doi: 10.1007/s00438-023-02059-5. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Mol Genet Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37555868 Review.
-
Single molecule fluorescence approaches shed light on intracellular RNAs.Chem Rev. 2014 Mar 26;114(6):3224-65. doi: 10.1021/cr400496q. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Chem Rev. 2014. PMID: 24417544 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- St Johnston D. Moving messages: The intracellular localization of mRNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:363–375. - PubMed
-
- Kloc M, Zearfoss NR, Etkin LD. Mechanisms of subcellular mRNA localization. Cell. 2002;108:533–544. - PubMed
-
- Du TG, Schmid M, Jansen RP. Why cells move messages: The biological functions of mRNA localization. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2007;18:171–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

