(PS)2-v2: template-based protein structure prediction server
- PMID: 19878598
- PMCID: PMC2775752
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-366
(PS)2-v2: template-based protein structure prediction server
Abstract
Background: Template selection and target-template alignment are critical steps for template-based modeling (TBM) methods. To identify the template for the twilight zone of 15~25% sequence similarity between targets and templates is still difficulty for template-based protein structure prediction. This study presents the (PS)2-v2 server, based on our original server with numerous enhancements and modifications, to improve reliability and applicability.
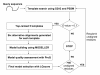
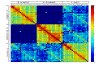
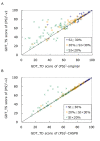
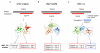
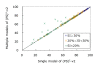
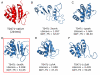
Results: To detect homologous proteins with remote similarity, the (PS)2-v2 server utilizes the S2A2 matrix, which is a 60 x 60 substitution matrix using the secondary structure propensities of 20 amino acids, and the position-specific sequence profile (PSSM) generated by PSI-BLAST. In addition, our server uses multiple templates and multiple models to build and assess models. Our method was evaluated on the Lindahl benchmark for fold recognition and ProSup benchmark for sequence alignment. Evaluation results indicated that our method outperforms sequence-profile approaches, and had comparable performance to that of structure-based methods on these benchmarks. Finally, we tested our method using the 154 TBM targets of the CASP8 (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction) dataset. Experimental results show that (PS)2-v2 is ranked 6th among 72 severs and is faster than the top-rank five serves, which utilize ab initio methods.
Conclusion: Experimental results demonstrate that (PS)2-v2 with the S2A2 matrix is useful for template selections and target-template alignments by blending the amino acid and structural propensities. The multiple-template and multiple-model strategies are able to significantly improve the accuracies for target-template alignments in the twilight zone. We believe that this server is useful in structure prediction and modeling, especially in detecting homologous templates with sequence similarity in the twilight zone.
Figures


Similar articles
-
(PS)2: protein structure prediction server.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 1;34(Web Server issue):W152-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl187. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16844981 Free PMC article.
-
MULTICOM2 open-source protein structure prediction system powered by deep learning and distance prediction.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 23;11(1):13155. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92395-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34162922 Free PMC article.
-
DescFold: a web server for protein fold recognition.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Dec 14;10:416. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-416. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 20003426 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence comparison and protein structure prediction.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006 Jun;16(3):374-84. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.05.006. Epub 2006 May 19. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006. PMID: 16713709 Review.
-
General overview on structure prediction of twilight-zone proteins.Theor Biol Med Model. 2015 Sep 4;12:15. doi: 10.1186/s12976-015-0014-1. Theor Biol Med Model. 2015. PMID: 26338054 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural view of a non Pfam singleton and crystal packing analysis.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31673. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031673. Epub 2012 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363703 Free PMC article.
-
Computational analysis of a novel mutation in ETFDH gene highlights its long-range effects on the FAD-binding motif.BMC Struct Biol. 2011 Oct 21;11:43. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-11-43. BMC Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 22013910 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of PAS domains and PAS-containing genes in eukaryotes.Chromosoma. 2014 Aug;123(4):385-405. doi: 10.1007/s00412-014-0457-x. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Chromosoma. 2014. PMID: 24699836
-
Another cat and mouse game: Deciphering the evolution of the SCGB superfamily and exploring the molecular similarity of major cat allergen Fel d 1 and mouse ABP using computational approaches.PLoS One. 2018 May 17;13(5):e0197618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197618. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29771985 Free PMC article.
-
Predicted Cold Shock Proteins from the Extremophilic Bacterium Deinococcus maricopensis and Related Deinococcus Species.Int J Microbiol. 2017;2017:5231424. doi: 10.1155/2017/5231424. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Int J Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29098004 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

