Uncovering small RNA-mediated responses to phosphate deficiency in Arabidopsis by deep sequencing
- PMID: 19854858
- PMCID: PMC2785986
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.147280
Uncovering small RNA-mediated responses to phosphate deficiency in Arabidopsis by deep sequencing
Abstract
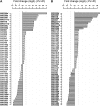
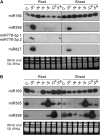
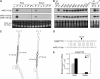
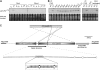
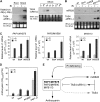
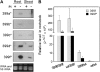
Recent studies have demonstrated the important role of plant microRNAs (miRNAs) under nutrient deficiencies. In this study, deep sequencing of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) small RNAs was conducted to reveal miRNAs and other small RNAs that were differentially expressed in response to phosphate (Pi) deficiency. About 3.5 million sequence reads corresponding to 0.6 to 1.2 million unique sequence tags from each Pi-sufficient or Pi-deficient root or shoot sample were mapped to the Arabidopsis genome. We showed that upon Pi deprivation, the expression of miR156, miR399, miR778, miR827, and miR2111 was induced, whereas the expression of miR169, miR395, and miR398 was repressed. We found cross talk coordinated by these miRNAs under different nutrient deficiencies. In addition to miRNAs, we identified one Pi starvation-induced DICER-LIKE1-dependent small RNA derived from the long terminal repeat of a retrotransposon and a group of 19-nucleotide small RNAs corresponding to the 5' end of tRNA and expressed at a high level in Pi-starved roots. Importantly, we observed an increased abundance of TAS4-derived trans-acting small interfering RNAs (ta-siRNAs) in Pi-deficient shoots and uncovered an autoregulatory mechanism of PAP1/MYB75 via miR828 and TAS4-siR81(-) that regulates the biosynthesis of anthocyanin. This finding sheds light on the regulatory network between miRNA/ta-siRNA and its target gene. Of note, a substantial amount of miR399* accumulated under Pi deficiency. Like miR399, miR399* can move across the graft junction, implying a potential biological role for miR399*. This study represents a comprehensive expression profiling of Pi-responsive small RNAs and advances our understanding of the regulation of Pi homeostasis mediated by small RNAs.
Figures
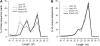

Similar articles
-
An autoregulatory feedback loop involving PAP1 and TAS4 in response to sugars in Arabidopsis.Plant Mol Biol. 2012 Sep;80(1):117-29. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9778-9. Epub 2011 May 1. Plant Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 21533841 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of nitrogen starvation-responsive microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048951. Epub 2012 Nov 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23155433 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA778 and SUVH6 are involved in phosphate homeostasis in Arabidopsis.Plant Sci. 2015 Sep;238:273-85. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.06.020. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26259194
-
The role of mobile small RNA species during root growth and development.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;24(2):211-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2011.12.005. Epub 2012 Jan 5. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22227227 Review.
-
miRNAs in the biogenesis of trans-acting siRNAs in higher plants.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010 Oct;21(8):798-804. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.03.008. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20359543 Review.
Cited by
-
Description of plant tRNA-derived RNA fragments (tRFs) associated with argonaute and identification of their putative targets.Biol Direct. 2013 Feb 12;8:6. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-8-6. Biol Direct. 2013. PMID: 23402430 Free PMC article.
-
Small tandem target mimic-mediated blockage of microRNA858 induces anthocyanin accumulation in tomato.Planta. 2015 Jul;242(1):283-93. doi: 10.1007/s00425-015-2305-5. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Planta. 2015. PMID: 25916310
-
The miR408a-BBP-LAC3/CSD1 module regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis mediated by crosstalk between copper homeostasis and ROS homeostasis during light induction in Malus plants.J Adv Res. 2023 Sep;51:27-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.11.005. Epub 2022 Nov 10. J Adv Res. 2023. PMID: 36371057 Free PMC article.
-
Unique expression, processing regulation, and regulatory network of peach (Prunus persica) miRNAs.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Aug 21;12:149. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-149. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 22909020 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and transcriptional responses of two contrasting Populus clones to nitrogen stress.Tree Physiol. 2016 May;36(5):628-42. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpw019. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Tree Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27095258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achard P, Herr A, Baulcombe DC, Harberd NP (2004) Modulation of floral development by a gibberellin-regulated microRNA. Development 131 3357–3365 - PubMed
-
- Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Carrington JC (2005) MicroRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 121 207–221 - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

