Activation of defense response pathways by OGs and Flg22 elicitors in Arabidopsis seedlings
- PMID: 19825551
- PMCID: PMC2954645
- DOI: 10.1093/mp/ssn019
Activation of defense response pathways by OGs and Flg22 elicitors in Arabidopsis seedlings
Erratum in
- Mol Plant. 2009 Jul;2(4):838
Abstract
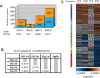
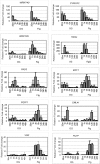
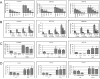
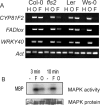
We carried out transcriptional profiling analysis in 10-d-old Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings treated with oligogalacturonides (OGs), oligosaccharides derived from the plant cell wall, or the bacterial flagellin peptide Flg22, general elicitors of the basal defense response in plants. Although detected by different receptors, both OGs and Flg22 trigger a fast and transient response that is both similar and comprehensive, and characterized by activation of early stages of multiple defense signaling pathways, particularly JA-associated processes. However, the response to Flg22 is stronger in both the number of genes differentially expressed and the amplitude of change. The magnitude of induction of individual genes is in both cases dose-dependent, but, even at very high concentrations, OGs do not induce a response that is as comprehensive as that seen with Flg22. While high doses of either microbe-associated molecular pattern (MAMP) elicit a late response that includes activation of senescence processes, SA-dependent secretory pathway genes and PR1 expression are substantially induced only by Flg22. These results suggest a lower threshold for activation of early responses than for sustained or SA-mediated late defenses. Expression patterns of amino-cyclopropane-carboxylate synthase genes also implicate ethylene biosynthesis in regulation of the late innate immune response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oligogalacturonide-auxin antagonism does not require posttranscriptional gene silencing or stabilization of auxin response repressors in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2011 Nov;157(3):1163-74. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.184663. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21880931 Free PMC article.
-
Immune responses induced by oligogalacturonides are differentially affected by AvrPto and loss of BAK1/BKK1 and PEPR1/PEPR2.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 May;18(4):582-595. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12419. Epub 2016 Jul 26. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27118426 Free PMC article.
-
The activated SA and JA signaling pathways have an influence on flg22-triggered oxidative burst and callose deposition.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 25;9(2):e88951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088951. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586453 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis MPK3 and MPK6 play different roles in basal and oligogalacturonide- or flagellin-induced resistance against Botrytis cinerea.Plant Physiol. 2011 Oct;157(2):804-14. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.174003. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21803860 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulose-Derived Oligomers Act as Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns and Trigger Defense-Like Responses.Plant Physiol. 2017 Apr;173(4):2383-2398. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.01680. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Plant Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28242654 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An experimental system to study responses of Medicago truncatula roots to chitin oligomers of high degree of polymerization and other microbial elicitors.Plant Cell Rep. 2013 Apr;32(4):489-502. doi: 10.1007/s00299-012-1380-3. Epub 2013 Jan 13. Plant Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23314495
-
Rhamnolipids elicit defense responses and induce disease resistance against biotrophic, hemibiotrophic, and necrotrophic pathogens that require different signaling pathways in Arabidopsis and highlight a central role for salicylic acid.Plant Physiol. 2012 Nov;160(3):1630-41. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.201913. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22968829 Free PMC article.
-
Microbe-associated molecular patterns-triggered root responses mediate beneficial rhizobacterial recruitment in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2012 Nov;160(3):1642-61. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.200386. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22972705 Free PMC article.
-
Plant immunity triggered by engineered in vivo release of oligogalacturonides, damage-associated molecular patterns.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 28;112(17):5533-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504154112. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25870275 Free PMC article.
-
Necrotroph attacks on plants: wanton destruction or covert extortion?Arabidopsis Book. 2010;8:e0136. doi: 10.1199/tab.0136. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Arabidopsis Book. 2010. PMID: 22303261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam L, Somerville SC. Genetic characterization of five powdery mildew disease resistance loci in Arabidopsis thalina. The Plant Journal. 1996;9:341–356. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JP, Badruzsaufari E, Schenk PM, Manners JM, Desmond OJ, Ehlert C, Maclean DJ, Ebert PR, Kazan K. Antagonistic interaction between abscisic acid and jasmonate-ethylene signaling pathways modulates defense gene expression and disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2004;16:3460–3479. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Argueso CT, Hansen M, Kieber JJ. Regulation of Ethylene Biosynthesis. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation. 2007;26:92–105.
-
- Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu WL, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, Sheen J. MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature. 2002;415:977–983. - PubMed
-
- Aziz A, Heyraud A, Lambert B. Oligogalacturonide signal transduction, induction of defense-related responses and protection of grapevine against Botrytis cinerea. Planta. 2004;218:767–774. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

