Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A bypasses p53 inactivation in a MYC model of lymphomagenesis
- PMID: 19815507
- PMCID: PMC2764894
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0907994106
Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A bypasses p53 inactivation in a MYC model of lymphomagenesis
Abstract
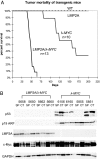
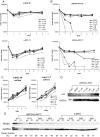
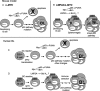
Although Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is linked to Burkitt's lymphoma (BL), the role of the virus in lymphomagenesis is unclear. LMP2A, encoded by EBV, can be detected in BL biopsies and has prosurvival functions. We generated mice expressing MYC and LMP2A in B cells. LMP2A/lambda-MYC mice show greatly accelerated tumor onset. Similar to previous work, we found p53 mutations in lambda-MYC tumors; however, we detected no mutations in the rapidly arising LMP2A/lambda-MYC tumors. We further demonstrate that the p53 pathway is functionally intact in LMP2A/lambda-MYC tumors, which have increased levels of PUMA and sensitivity to p53 activation by Nutlin. This work shows that LMP2A can permit tumorigenesis in the presence of an intact p53 pathway, identifying an important contribution of EBV to BL.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two Pathways of p27Kip1 Degradation Are Required for Murine Lymphoma Driven by Myc and EBV Latent Membrane Protein 2A.mBio. 2019 Apr 16;10(2):e00548-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00548-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30992353 Free PMC article.
-
Latent membrane proteins from EBV differentially target cellular pathways to accelerate MYC-induced lymphomagenesis.Blood Adv. 2022 Jul 26;6(14):4283-4296. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022007695. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 35605249 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A accelerates MYC-induced lymphomagenesis.Oncogene. 2009 Mar 19;28(11):1471-6. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.492. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19182823 Free PMC article.
-
EBNA2 and c-myc in B cell immortalization by Epstein-Barr virus and in the pathogenesis of Burkitt's lymphoma.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1999;246:315-20; discussion 321. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-60162-0_39. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10396071 Review. No abstract available.
-
Role of Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt's lymphoma.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001;258:141-51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56515-1_9. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11443859 Review.
Cited by
-
Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1) and LMP2A Collaborate To Promote Epstein-Barr Virus-Induced B Cell Lymphomas in a Cord Blood-Humanized Mouse Model but Are Not Essential.J Virol. 2017 Mar 13;91(7):e01928-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01928-16. Print 2017 Apr 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28077657 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A reduces hyperactivation induced by LMP1 to restore normal B cell phenotype in transgenic mice.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(4):e1002662. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002662. Epub 2012 Apr 19. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22536156 Free PMC article.
-
EBV germinates lymphoma from the germinal center in a battle with T and NK cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 May 2;114(18):4571-4573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1704102114. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28442562 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dasatinib therapy results in decreased B cell proliferation, splenomegaly, and tumor growth in a murine model of lymphoma expressing Myc and Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A.Antiviral Res. 2012 Jul;95(1):49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.05.003. Epub 2012 May 16. Antiviral Res. 2012. PMID: 22609829 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 2A (LMP2A) Enhances ATP Production in B Cell Tumors through mTOR and HIF-1α.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 2;25(7):3944. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073944. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Epstein MA, Achong BG, Barr YM. Virus particles in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt's lymphoma. Lancet. 1964;1:702–703. - PubMed
-
- Kelly GL, Rickinson AB. Burkitt lymphoma: Revisiting the pathogenesis of a virus-associated malignancy. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2007;2007:277–284. - PubMed
-
- Pelengaris S, Khan M, Evan G. c-MYC: More than just a matter of life and death. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:764–776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

