An overview of the molecular mechanism of autophagy
- PMID: 19802558
- PMCID: PMC2832191
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-00302-8_1
An overview of the molecular mechanism of autophagy
Abstract
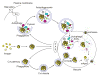
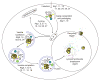
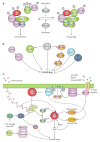
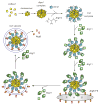
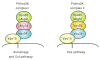
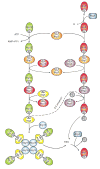
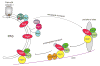
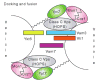
Autophagy is a highly conserved cellular degradation process in which portions of cytosol and organelles are sequestered into a double-membrane vesicle, an autophagosome, and delivered into a degradative organelle, the vacuole/lysosome, for breakdown and eventual recycling of the resulting macromolecules. This process relieves the cell from various stress conditions. Autophagy plays a critical role during cellular development and differentiation, functions in tumor suppression, and may be linked to life span extension. Autophagy also has diverse roles in innate and adaptive immunity, such as resistance to pathogen invasion. Substantial progress has been made in the identification of many autophagy-related (ATG) genes that are essential to drive this cellular process, including both selective and nonselective types of autophagy. Identification of the ATG genes in yeast, and the finding of orthologs in other organisms, reveals the conservation of the autophagic machinery in all eukaryotes. Here, we summarize our current knowledge about the machinery and molecular mechanism of autophagy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Autophagy: molecular machinery for self-eating.Cell Death Differ. 2005 Nov;12 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):1542-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401765. Cell Death Differ. 2005. PMID: 16247502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular mechanism of autophagy.Mol Med. 2003 Mar-Apr;9(3-4):65-76. Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 12865942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular machinery of autophagy: unanswered questions.J Cell Sci. 2005 Jan 1;118(Pt 1):7-18. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01620. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15615779 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of macroautophagy in yeast.J Mol Biol. 2016 May 8;428(9 Pt A):1681-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.02.021. Epub 2016 Feb 22. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26908221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective types of autophagy in yeast.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Sep;1793(9):1404-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.02.006. Epub 2009 Mar 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19264099 Review.
Cited by
-
An overview of autophagy: morphology, mechanism, and regulation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Jan 20;20(3):460-73. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5371. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 23725295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic identification of signal integration by protein kinase A.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 7;112(14):4501-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1409938112. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25831502 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-ΔNp63α-dependent regulation of autophagic signaling through transcription and micro-RNA modulation.Cell Cycle. 2012 Mar 15;11(6):1247-59. doi: 10.4161/cc.11.6.19670. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22356768 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen and its metabolism: some new developments and old themes.Biochem J. 2012 Feb 1;441(3):763-87. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111416. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22248338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual role of autophagy in HIV-1 replication and pathogenesis.AIDS Res Ther. 2012 May 20;9(1):16. doi: 10.1186/1742-6405-9-16. AIDS Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22606989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arico S, Petiot A, Bauvy C, Dubbelhuis PF, Meijer AJ, Codogno P, Ogier-Denis E. The tumor suppressor PTEN positively regulates macroautophagy by inhibiting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:35243–35246. - PubMed
-
- Bellu AR, Komori M, van der Klei IJ, Kiel JAKW, Veenhuis M. Peroxisome biogenesis and selective degradation converge at Pex14p. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:44570–44574. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

