CGI-58/ABHD5 is a coenzyme A-dependent lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase
- PMID: 19801371
- PMCID: PMC2842141
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M001917
CGI-58/ABHD5 is a coenzyme A-dependent lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase
Abstract
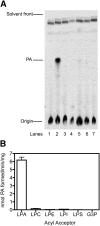
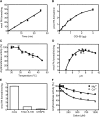
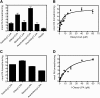
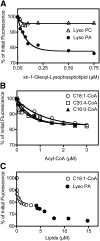
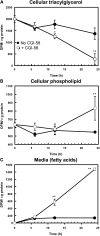
Mutations in human CGI-58/ABHD5 cause Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome (CDS), characterized by excessive storage of triacylglycerol in tissues. CGI-58 is an alpha/beta-hydrolase fold enzyme expressed in all vertebrates. The carboxyl terminus includes a highly conserved consensus sequence (HXXXXD) for acyltransferase activity. Mouse CGI-58 was expressed in Escherichia coli as a fusion protein with two amino terminal 6-histidine tags. Recombinant CGI-58 displayed acyl-CoA-dependent acyltransferase activity to lysophosphatidic acid, but not to other lysophospholipid or neutral glycerolipid acceptors. Production of phosphatidic acid increased with time and increasing concentrations of recombinant CGI-58 and was optimal between pH 7.0 and 8.5. The enzyme showed saturation kinetics with respect to 1-oleoyl-lysophosphatidic acid and oleoyl-CoA and preference for arachidonoyl-CoA and oleoyl-CoA. The enzyme showed slight preference for 1-oleoyl lysophosphatidic acid over 1-palmitoyl, 1-stearoyl, or 1-arachidonoyl lysophosphatidic acid. Recombinant CGI-58 showed intrinsic fluorescence for tryptophan that was quenched by the addition of 1-oleoyl-lysophosphatidic acid, oleoyl-CoA, arachidonoyl-CoA, and palmitoyl-CoA, but not by lysophosphatidyl choline. Expression of CGI-58 in fibroblasts from humans with CDS increased the incorporation of radiolabeled fatty acids released from the lipolysis of stored triacylglycerols into phospholipids. CGI-58 is a CoA-dependent lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase that channels fatty acids released from the hydrolysis of stored triacylglycerols into phospholipids.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative gene identification 58/α/β hydrolase domain 5 lacks lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase activity.J Lipid Res. 2014 Aug;55(8):1750-61. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M051151. Epub 2014 May 30. J Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24879803 Free PMC article.
-
CGI-58, the causative gene for Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome, mediates acylation of lysophosphatidic acid.J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 5;283(36):24525-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801783200. Epub 2008 Jul 7. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18606822 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative gene identification-58 (CGI-58) promotes autophagy as a putative lysophosphatidylglycerol acyltransferase.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 21;289(47):33044-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.573857. Epub 2014 Oct 14. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25315780 Free PMC article.
-
The important role of epidermal triacylglycerol metabolism for maintenance of the skin permeability barrier function.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Mar;1841(3):409-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23928127 Review.
-
Critical roles for α/β hydrolase domain 5 (ABHD5)/comparative gene identification-58 (CGI-58) at the lipid droplet interface and beyond.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017 Oct;1862(10 Pt B):1233-1241. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.07.016. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017. PMID: 28827091 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional cardiac lipolysis in mice critically depends on comparative gene identification-58.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 5;288(14):9892-9904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.420620. Epub 2013 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23413028 Free PMC article.
-
Structure/function relationships of adipose phospholipase A2 containing a cys-his-his catalytic triad.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 12;287(42):35260-35274. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.398859. Epub 2012 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22923616 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct cellular pools of perilipin 5 point to roles in lipid trafficking.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Feb;1821(2):268-78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.10.017. Epub 2011 Oct 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22063271 Free PMC article.
-
The α/β-hydrolase domain-containing 4- and 5-related phospholipase Pummelig controls energy storage in Drosophila.J Lipid Res. 2019 Aug;60(8):1365-1378. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M092817. Epub 2019 Jun 4. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 31164391 Free PMC article.
-
An ER phospholipid hydrolase drives ER-associated mitochondrial constriction for fission and fusion.Elife. 2022 Nov 30;11:e84279. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84279. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36448541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brasaemle D. L.2007. Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. The perilipin family of structural lipid droplet proteins: stabilization of lipid droplets and control of lipolysis. J. Lipid Res. 48: 2547–2559 - PubMed
-
- Lefevre C., Jobard F., Caux F., Bouadjar B., Karaduman A., Heilig R., Lakhdar H., Wollenberg A., Verret J. L., Weissenbach J., et al. 2001. Mutations in CGI-58, the gene encoding a new protein of the esterase/lipase/thioesterase subfamily, in Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 69: 1002–1012 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Igal R. A., Rhoads J. M., Coleman R. A. 1997. Neutral lipid storage disease with fatty liver and cholestasis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 25: 541–547 - PubMed
-
- Srebrnik A., Brenner S., Ilie B., Messer G. 1998. Dorfman-Chanarin syndrome: morphologic studies and presentation of new cases. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 20: 79–85 - PubMed
-
- Wollenberg A., Geiger E., Schaller M., Wolff H. 2000. Dorfman-Chanarin syndrome in a Turkish kindred: conductor diagnosis requires analysis of multiple eosinophils. Acta Derm. Venereol. 80: 39–43 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

