Invasive and indigenous microbiota impact intestinal stem cell activity through multiple pathways in Drosophila
- PMID: 19797770
- PMCID: PMC2758745
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1827009
Invasive and indigenous microbiota impact intestinal stem cell activity through multiple pathways in Drosophila
Abstract
Gut homeostasis is controlled by both immune and developmental mechanisms, and its disruption can lead to inflammatory disorders or cancerous lesions of the intestine. While the impact of bacteria on the mucosal immune system is beginning to be precisely understood, little is known about the effects of bacteria on gut epithelium renewal. Here, we addressed how both infectious and indigenous bacteria modulate stem cell activity in Drosophila. We show that the increased epithelium renewal observed upon some bacterial infections is a consequence of the oxidative burst, a major defense of the Drosophila gut. Additionally, we provide evidence that the JAK-STAT (Janus kinase-signal transducers and activators of transcription) and JNK (c-Jun NH(2) terminal kinase) pathways are both required for bacteria-induced stem cell proliferation. Similarly, we demonstrate that indigenous gut microbiota activate the same, albeit reduced, program at basal levels. Altered control of gut microbiota in immune-deficient or aged flies correlates with increased epithelium renewal. Finally, we show that epithelium renewal is an essential component of Drosophila defense against oral bacterial infection. Altogether, these results indicate that gut homeostasis is achieved by a complex interregulation of the immune response, gut microbiota, and stem cell activity.
Figures
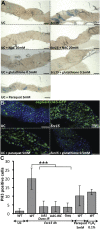
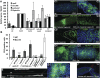
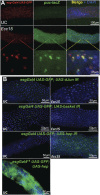
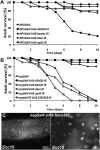
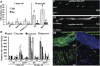
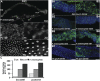
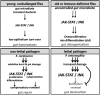
Comment in
-
Bacterial-modulated host immunity and stem cell activation for gut homeostasis.Genes Dev. 2009 Oct 1;23(19):2260-5. doi: 10.1101/gad.1858709. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19797765 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Autocrine and paracrine unpaired signaling regulate intestinal stem cell maintenance and division.J Cell Sci. 2012 Dec 15;125(Pt 24):5944-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113100. Epub 2012 Oct 4. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 23038775
-
The UPD3 cytokine couples environmental challenge and intestinal stem cell division through modulation of JAK/STAT signaling in the stem cell microenvironment.Dev Biol. 2013 Jan 15;373(2):383-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.10.023. Epub 2012 Oct 27. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23110761 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila EGFR pathway coordinates stem cell proliferation and gut remodeling following infection.BMC Biol. 2010 Dec 22;8:152. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-152. BMC Biol. 2010. PMID: 21176204 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal stem cell asymmetric division in the Drosophila posterior midgut.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Sep;224(3):581-4. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22194. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20578235 Review.
-
Drosophila Jak/STAT Signaling: Regulation and Relevance in Human Cancer and Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 14;19(12):4056. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124056. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30558204 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drosophila Caliban preserves intestinal homeostasis and lifespan through regulating mitochondrial dynamics and redox state in enterocytes.PLoS Genet. 2020 Oct 15;16(10):e1009140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009140. eCollection 2020 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 33057338 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal barrier dysfunction links metabolic and inflammatory markers of aging to death in Drosophila.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 26;109(52):21528-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215849110. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23236133 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila models of epithelial stem cells and their niches.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012 May-Jun;1(3):447-57. doi: 10.1002/wdev.36. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 23801493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between the microbiome and mating influence the female's transcriptional profile in Drosophila melanogaster.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 23;10(1):18168. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75156-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33097776 Free PMC article.
-
Organ-specific mediation of lifespan extension: more than a gut feeling?Ageing Res Rev. 2013 Jan;12(1):436-44. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2012.05.003. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Ageing Res Rev. 2013. PMID: 22706186 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agaisse H, Petersen UM, Boutros M, Mathey-Prevot B, Perrimon N. Signaling role of hemocytes in Drosophila JAK/STAT-dependent response to septic injury. Dev Cell. 2003;5:441–450. - PubMed
-
- Bach EA, Ekas LA, Ayala-Camargo A, Flaherty MS, Lee H, Perrimon N, Baeg GH. GFP reporters detect the activation of the Drosophila JAK/STAT pathway in vivo. Gene Expr Patterns. 2007;7:323–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
