Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances the expression of the monocarboxylate transporter 2 through translational activation in mouse cultured cortical neurons
- PMID: 19794395
- PMCID: PMC2949129
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.208
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances the expression of the monocarboxylate transporter 2 through translational activation in mouse cultured cortical neurons
Abstract
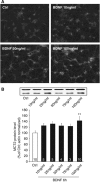
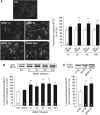
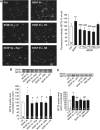
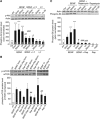
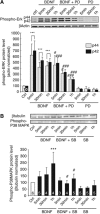
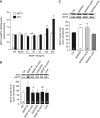
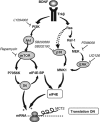
MCT2 is the predominant neuronal monocarboxylate transporter allowing lactate use as an alternative energy substrate. It is suggested that MCT2 is upregulated to meet enhanced energy demands after modifications in synaptic transmission. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a promoter of synaptic plasticity, significantly increased MCT2 protein expression in cultured cortical neurons (as shown by immunocytochemistry and western blot) through a translational regulation at the synaptic level. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor can cause translational activation through different signaling pathways. Western blot analyses showed that p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), Akt, and S6 were strongly phosphorylated on BDNF treatment. To determine by which signal transduction pathway(s) BDNF mediates its upregulation of MCT2 protein expression, the effect of specific inhibitors for p38 MAPK, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase (MEK), p44/p42 MAPK (ERK), and Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) was evaluated. It could be observed that the BDNF-induced increase in MCT2 protein expression was almost completely blocked by all inhibitors, except for JAK2. These data indicate that BDNF induces an increase in neuronal MCT2 protein expression by a mechanism involving a concomitant stimulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/S6, p38 MAPK, and p44/p42 MAPK. Moreover, our observations suggest that changes in MCT2 expression could participate in the process of synaptic plasticity induced by BDNF.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noradrenaline enhances the expression of the neuronal monocarboxylate transporter MCT2 by translational activation via stimulation of PI3K/Akt and the mTOR/S6K pathway.J Neurochem. 2007 Jul;102(2):389-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04495.x. Epub 2007 Mar 29. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17394554
-
Insulin and IGF-1 enhance the expression of the neuronal monocarboxylate transporter MCT2 by translational activation via stimulation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin pathway.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Jan;27(1):53-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05981.x. Epub 2007 Dec 15. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18093179
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances the hippocampal expression of key postsynaptic proteins in vivo including the monocarboxylate transporter MCT2.Neuroscience. 2011 Sep 29;192:155-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.06.059. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21736920
-
BDNF-induced local protein synthesis and synaptic plasticity.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:639-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23602987 Review.
-
BDNF mechanisms in late LTP formation: A synthesis and breakdown.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:664-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23831365 Review.
Cited by
-
Lactate transport and signaling in the brain: potential therapeutic targets and roles in body-brain interaction.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015 Feb;35(2):176-85. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.206. Epub 2014 Nov 26. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015. PMID: 25425080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactate as Potential Mediators for Exercise-Induced Positive Effects on Neuroplasticity and Cerebrovascular Plasticity.Front Physiol. 2021 Jul 5;12:656455. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.656455. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34290615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cortical Bilateral Adaptations in Rats Submitted to Focal Cerebral Ischemia: Emphasis on Glial Metabolism.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Mar;55(3):2025-2041. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0458-x. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28271402
-
Elevated glutamate and lactate predict brain death after severe head trauma.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2017 May 4;4(6):392-402. doi: 10.1002/acn3.416. eCollection 2017 Jun. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28589166 Free PMC article.
-
Application of custom-designed oligonucleotide array CGH in 145 patients with autistic spectrum disorders.Eur J Hum Genet. 2013 Jun;21(6):620-5. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.219. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23032108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almeida RD, Manadas BJ, Melo CV, Gomes JR, Mendes CS, Graos MM, Carvalho RF, Carvalho AP, Duarte CB. Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12:1329–1343. - PubMed
-
- Bergersen L, Rafiki A, Ottersen OP. Immunogold cytochemistry identifies specialized membrane domains for monocarboxylate transport in the central nervous system. Neurochem Res. 2002;27:89–96. - PubMed
-
- Bergersen LH, Magistretti PJ, Pellerin L. Selective postsynaptic co-localization of MCT2 with AMPA receptor GluR2/3 subunits at excitatory synapses exhibiting AMPA receptor trafficking. Cereb Cortex. 2005;15:361–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

