NRF2 cysteine residues are critical for oxidant/electrophile-sensing, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1-dependent ubiquitination-proteasomal degradation, and transcription activation
- PMID: 19786557
- PMCID: PMC2784728
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.109.058453
NRF2 cysteine residues are critical for oxidant/electrophile-sensing, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1-dependent ubiquitination-proteasomal degradation, and transcription activation
Abstract
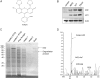
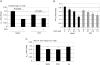
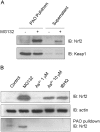
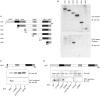
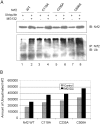
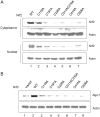
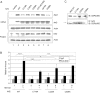
Cells respond to oxidants and electrophiles by activating receptor/transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) to coordinate the induction of cytoprotective genes critical for defense against oxidative and other stresses. Activation involves blocking the ubiquitination-proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Modification of cysteine thiol groups by inducers in the linker region of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1 (Keap1), which congregates Nrf2 into the Keap1/Cul3 E3 complex for ubiquitination, is important but not sufficient for activation of Nrf2. Here we show that evolutionarily conserved cysteine residues of Nrf2 are critical for Nrf2 regulation. FlAsH (an arsenic-based fluorophore) and phenylarsine oxide (PAO) potently induce Nrf2 target genes and bind to Nrf2 in vitro and in vivo. Binding is inhibited by prototypical inducers arsenic and tert-butylhydroquinone. PAO affinity pull-down and mutation of individual cysteine to alanine reveal that Cys235, Cys311, Cys316, Cys414, and Cys506 are critical for binding, and binding is modulated by intramolecular interactions. To corroborate the functions of cysteine residues, Nrf2 wild-type or mutants are expressed in Nrf2 knockout cells to reconstitute Nrf2 regulation. Nrf2 mutants have reduced t(1/2) that inversely correlates with increased binding to Keap1 and polyubiquitination of mutant proteins. It is remarkable that the mutants fail to respond to arsenic for Nrf2 activation and gene induction. Furthermore, mutations at Cys119, Cys235, and Cys506 impede binding of Nrf2 to endogenous antioxidant response element and to coactivator cAMP response element-binding protein-binding protein/p300. The findings demonstrate that Nrf2 cysteine residues critically regulate oxidant/electrophile sensing, repress Keap1-dependent ubiquitination-proteasomal degradation, and promote recruitment of coactivators, such that chemical sensing, receptor activation, and transcription activation are integrated at the receptor molecule.
Figures
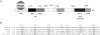




Similar articles
-
Critical cysteine residues of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 in arsenic sensing and suppression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Jan;332(1):66-75. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.160465. Epub 2009 Oct 6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 19808700 Free PMC article.
-
Cul3-mediated Nrf2 ubiquitination and antioxidant response element (ARE) activation are dependent on the partial molar volume at position 151 of Keap1.Biochem J. 2009 Jul 29;422(1):171-80. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090471. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19489739 Free PMC article.
-
Specific patterns of electrophile adduction trigger Keap1 ubiquitination and Nrf2 activation.J Biol Chem. 2005 Sep 9;280(36):31768-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503346200. Epub 2005 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15985429
-
Cysteine-based regulation of the CUL3 adaptor protein Keap1.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010 Apr 1;244(1):21-6. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.06.016. Epub 2009 Jun 26. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19560482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keap1, the cysteine-based mammalian intracellular sensor for electrophiles and oxidants.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Mar 1;617:84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 27497696 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Redox homeostasis: the linchpin in stem cell self-renewal and differentiation.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Mar 14;4(3):e537. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.50. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23492768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An unexplored role for Peroxiredoxin in exercise-induced redox signalling?Redox Biol. 2016 Aug;8:51-8. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.10.003. Epub 2015 Dec 25. Redox Biol. 2016. PMID: 26748042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013;53:401-26. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011112-140320. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23294312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A perspective on dietary phytochemicals and cancer chemoprevention: oxidative stress, nrf2, and epigenomics.Top Curr Chem. 2013;329:133-62. doi: 10.1007/128_2012_340. Top Curr Chem. 2013. PMID: 22836898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deficient expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 is consistent with increased sensitivity of Gorlin syndrome patients to radiation carcinogenesis.Mol Carcinog. 2015 Jun;54(6):473-84. doi: 10.1002/mc.22115. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Mol Carcinog. 2015. PMID: 24285572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aitken A, Learmonth M. (1996) Estimation of disulfide bonds using Ellman's reagent, in Protein Protocol Handbook (Walker JM. ed) pp 487–494, Humana Press, Inc, Totowa, NJ:
-
- Cho HY, Jedlicka AE, Reddy SP, Zhang LY, Kensler TW, Kleeberger SR. (2002) Linkage analysis of susceptibility to hyperoxia. Nrf2 is a candidate gene. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 26:42–51 - PubMed
-
- Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Cole RN, Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Yamamoto M, Talalay P. (2002) Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:11908–11913 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
