Integration of neuronal clones in the radial cortical columns by EphA and ephrin-A signalling
- PMID: 19759535
- PMCID: PMC2874978
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08362
Integration of neuronal clones in the radial cortical columns by EphA and ephrin-A signalling
Abstract
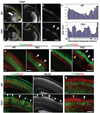
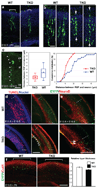
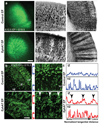
The cerebral cortex is a laminated sheet of neurons composed of the arrays of intersecting radial columns. During development, excitatory projection neurons originating from the proliferative units at the ventricular surface of the embryonic cerebral vesicles migrate along elongated radial glial fibres to form a cellular infrastructure of radial (vertical) ontogenetic columns in the overlaying cortical plate. However, a subpopulation of these clonally related neurons also undergoes a short lateral shift and transfers from their parental to the neighbouring radial glial fibres, and intermixes with neurons originating from neighbouring proliferative units. This columnar organization acts as the primary information processing unit in the cortex. The molecular mechanisms, role and significance of this lateral dispersion for cortical development are not understood. Here we show that an Eph receptor A (EphA) and ephrin A (Efna) signalling-dependent shift in the allocation of clonally related neurons is essential for the proper assembly of cortical columns. In contrast to the relatively uniform labelling of the developing cortical plate by various molecular markers and retrograde tracers in wild-type mice, we found alternating labelling of columnar compartments in Efna knockout mice that are caused by impaired lateral dispersion of migrating neurons rather than by altered cell production or death. Furthermore, in utero electroporation showed that lateral dispersion depends on the expression levels of EphAs and ephrin-As during neuronal migration. This so far unrecognized mechanism for lateral neuronal dispersion seems to be essential for the proper intermixing of neuronal types in the cortical columns, which, when disrupted, might contribute to neuropsychiatric disorders associated with abnormal columnar organization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ephrin signalling controls brain size by regulating apoptosis of neural progenitors.Nature. 2005 Jun 30;435(7046):1244-50. doi: 10.1038/nature03651. Epub 2005 May 15. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15902206
-
Neuronal migration and contact guidance in the primate telencephalon.Postgrad Med J. 1978;54 Suppl 1:25-40. Postgrad Med J. 1978. PMID: 364453 Review.
-
Cdk5 is required for multipolar-to-bipolar transition during radial neuronal migration and proper dendrite development of pyramidal neurons in the cerebral cortex.Development. 2007 Jun;134(12):2273-82. doi: 10.1242/dev.02854. Epub 2007 May 16. Development. 2007. PMID: 17507397
-
EphA family gene expression in the developing mouse neocortex: regional patterns reveal intrinsic programs and extrinsic influence.J Comp Neurol. 2003 Feb 10;456(3):203-16. doi: 10.1002/cne.10498. J Comp Neurol. 2003. PMID: 12528186
-
Should I stay or should I go? Ephs and ephrins in neuronal migration.Neurosignals. 2012;20(3):190-201. doi: 10.1159/000333784. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Neurosignals. 2012. PMID: 22456188 Review.
Cited by
-
Dendritic bundles, minicolumns, columns, and cortical output units.Front Neuroanat. 2010 Mar 12;4:11. doi: 10.3389/neuro.05.011.2010. eCollection 2010. Front Neuroanat. 2010. PMID: 20305751 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of FLRT2 in Postnatal Central Nervous System Development and After Spinal Cord Injury.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Oct 22;14:756264. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.756264. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34744626 Free PMC article.
-
Molecules and mechanisms that regulate multipolar migration in the intermediate zone.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Nov 14;8:386. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00386. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25452716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subcellular localization and function of mouse radial spoke protein 3 in mammalian cells and central nervous system.J Mol Histol. 2014 Dec;45(6):723-32. doi: 10.1007/s10735-014-9590-3. Epub 2014 Jul 31. J Mol Histol. 2014. PMID: 25079589
-
From genes to folds: a review of cortical gyrification theory.Brain Struct Funct. 2015 Sep;220(5):2475-83. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0961-z. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Brain Struct Funct. 2015. PMID: 25511709 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mountcastle VB. The columnar organization of the neocortex. Brain. 1997;120:701–722. - PubMed
-
- Szentágothai J. The Ferrier Lecture, 1977. The neuron network of the cerebral cortex: a functional interpretation. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978;201:219–248. - PubMed
-
- Goldman-Rakic PS. Circuitry of primate prefrontal cortex and regulation of behavior by representational memory. In: Plum F, editor. Handbook of Physiology, The Nervous System, Higher Functions of the Brain. Bethesda: Am. Physiol. Soc.; 1987. pp. 373–417.
-
- Rakic P. Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex. J. Comp. Neurol. l972;l45:6l–84. - PubMed
-
- Rakic P. Specification of cerebral cortical areas. Science. 1988;241:170–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS014841/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS014841-31/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS038296-10/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS038296/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA022785/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA022785-03/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS038296-09/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA023999-02/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA023999/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS014841-30/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA023999/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA023999-01A1/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

