PYK2/PDZ-RhoGEF links Ca2+ signaling to RhoA
- PMID: 19759375
- PMCID: PMC3939713
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.190892
PYK2/PDZ-RhoGEF links Ca2+ signaling to RhoA
Abstract
Objective: Ras homolog gene family member A (RhoA)/Rho-kinase-mediated Ca(2+) sensitization is a critical component of constrictor responses. The present study investigates how angiotensin II activates RhoA.
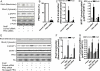
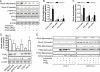
Methods and results: Adenoviral vectors were used to manipulate the expression of regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) domain containing Rho-specific guanine exchange factors (RhoGEFs) and proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (PYK2), a nonreceptor tyrosine kinase, in primary rat vascular smooth muscle cells. As an evidence of RhoA activation, RhoA translocation and MYPT1 (the regulatory subunit of myosin light chain phosphatase) phosphorylation were analyzed by Western blot. Results showed that overexpression of PDZ-RhoGEF, but not p115-RhoGEF or leukemia-associated RhoGEF (LARG), enhanced RhoA activation by angiotensin II. Knockdown of PDZ-RhoGEF decreased RhoA activation by angiotensin II. PDZ-RhoGEF was phosphorylated and activated by PYK2 in vitro, and knockdown of PDZ-RhoGEF reduced RhoA activation by constitutively active PYK2, indicating that PDZ-RhoGEF links PYK2 to RhoA. Knockdown of PYK2 or PDZ-RhoGEF markedly decreased RhoA activation by A23187, a Ca(2+) ionophore, demonstrating that PYK2/PDZ-RhoGEF couples RhoA activation to Ca(2+).
Conclusions: PYK2 and PDZ-RhoGEF are necessary for angiotensin II-induced RhoA activation and for Ca(2+) signaling to RhoA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II up-regulates the leukemia-associated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (RhoGEF), a regulator of G protein signaling domain-containing RhoGEF, in vascular smooth muscle cells.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Mar;69(3):932-40. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.017830. Epub 2005 Dec 14. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16354763
-
Leukemia-associated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor promotes G alpha q-coupled activation of RhoA.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jun;22(12):4053-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.12.4053-4061.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12024019 Free PMC article.
-
Increased PDZ-RhoGEF/RhoA/Rho kinase signaling in small mesenteric arteries of angiotensin II-induced hypertensive rats.J Hypertens. 2007 Aug;25(8):1687-97. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32816f778d. J Hypertens. 2007. PMID: 17620967
-
A role for the Ca(2+)-dependent tyrosine kinase Pyk2 in tonic depolarization-induced vascular smooth muscle contraction.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2015 Dec;36(6):479-89. doi: 10.1007/s10974-015-9416-2. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2015. PMID: 26150074 Review.
-
Phosphorylation-mediated regulation of GEFs for RhoA.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(1):11-8. doi: 10.4161/cam.28058. Epub 2013 Jan 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 24589508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane depolarization-induced RhoA/Rho-associated kinase activation and sustained contraction of rat caudal arterial smooth muscle involves genistein-sensitive tyrosine phosphorylation.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2013;49:26-45. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.49.26. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2013. PMID: 24133693 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent modulation of Rho-kinase and Ca(2+) influx pathways by Src family kinases and focal adhesion kinase in airway smooth muscle.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;172(22):5265-80. doi: 10.1111/bph.13313. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26294392 Free PMC article.
-
Non-receptor-tyrosine kinases integrate fast glucocorticoid signaling in hippocampal neurons.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 16;288(33):23725-39. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.470146. Epub 2013 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23818519 Free PMC article.
-
Druggable targets in the Rho pathway and their promise for therapeutic control of blood pressure.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Jan;193:121-134. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30189292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Magnetic Field Gradient and Gadolinium-Based MRI Contrast Agent Dotarem on Mouse Macrophages.Cells. 2022 Feb 22;11(5):757. doi: 10.3390/cells11050757. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hai CM, Murphy RA. Ca2+, crossbridge phosphorylation, and contraction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:285–298. - PubMed
-
- Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV. Ca2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: modulated by G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:1325–1358. - PubMed
-
- Uehata M, Ishizaki T, Satoh H, Ono T, Kawahara T, Morishita T, Tamakawa H, Yamagami K, Inui J, Maekawa M, Narumiya S. Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. Nature. 1997;389:990–994. - PubMed
-
- Kanda T, Wakino S, Homma K, Yoshioka K, Tatematsu S, Hasegawa K, Takamatsu I, Sugano N, Hayashi K, Saruta T. Rho-kinase as a molecular target for insulin resistance and hypertension. Faseb J. 2006;20:169–171. - PubMed
-
- Bos JL, Rehmann H, Wittinghofer A. GEFs and GAPs: critical elements in the control of small G proteins. Cell. 2007;129:865–877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL071138-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL074167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-74167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL074167-050005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL074167-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071138-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071138-05A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-71138/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071138-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071138-01A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071138/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071138-06/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

