The endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP/GRP78 is important in the structure and function of the human cytomegalovirus assembly compartment
- PMID: 19741001
- PMCID: PMC2772683
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00762-09
The endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP/GRP78 is important in the structure and function of the human cytomegalovirus assembly compartment
Abstract
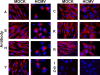
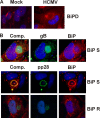
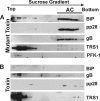
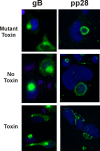
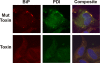
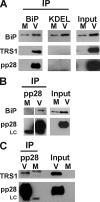
We previously demonstrated that the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone BiP functions in human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) assembly and egress. Here, we show that BiP localizes in two cytoplasmic structures in infected cells. Antibodies to the extreme C terminus, which includes BiP's KDEL ER localization sequence, detect BiP in regions of condensed ER near the periphery of the cell. Antibodies to the full length, N terminus, or larger portion of the C terminus detect BiP in the assembly compartment. This inability of C-terminal antibodies to detect BiP in the assembly compartment suggests that BiP's KDEL sequence is occluded in the assembly compartment. Depletion of BiP causes the condensed ER and assembly compartments to dissociate, indicating that BiP is important for their integrity. BiP and pp28 are in association in the assembly compartment, since antibodies that detect BiP in the assembly compartment coimmunoprecipitate pp28 and vice versa. In addition, BiP and pp28 copurify with other assembly compartment components on sucrose gradients. BiP also coimmunoprecipitates TRS1. Previous data show that cells infected with a TRS1-deficient virus have cytoplasmic and assembly compartment defects like those seen when BiP is depleted. We show that a fraction of TRS1 purifies with the assembly compartment. These findings suggest that BiP and TRS1 share a function in assembly compartment maintenance. In summary, BiP is diverted from the ER to associate with pp28 and TRS1, contributing to the integrity and function of the assembly compartment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP, SUN domain proteins, and dynein in altering nuclear morphology during human cytomegalovirus infection.J Virol. 2010 Jul;84(14):7005-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00719-10. Epub 2010 May 19. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20484513 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus specifically controls the levels of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP/GRP78, which is required for virion assembly.J Virol. 2008 Jan;82(1):31-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01881-07. Epub 2007 Oct 17. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 17942541 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence requirements for localization of human cytomegalovirus tegument protein pp28 to the virus assembly compartment and for assembly of infectious virus.J Virol. 2006 Jun;80(11):5611-26. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02630-05. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16699042 Free PMC article.
-
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone BiP is a master regulator of ER functions: Getting by with a little help from ERdj friends.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 8;294(6):2098-2108. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV118.002804. Epub 2018 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30563838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HSPA5 Gene encoding Hsp70 chaperone BiP in the endoplasmic reticulum.Gene. 2017 Jun 30;618:14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.03.005. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28286085 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human cytomegalovirus infection interferes with the maintenance and differentiation of trophoblast progenitor cells of the human placenta.J Virol. 2015 May;89(9):5134-47. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03674-14. Epub 2015 Mar 4. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25741001 Free PMC article.
-
Viral use and subversion of membrane organization and trafficking.J Cell Sci. 2021 Mar 4;134(5):jcs252676. doi: 10.1242/jcs.252676. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 33664154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human cytomegalovirus protein pUL38 suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cell death independently of its ability to induce mTORC1 activation.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(17):9103-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00572-11. Epub 2011 Jun 29. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21715486 Free PMC article.
-
Viral and host control of cytomegalovirus maturation.Trends Microbiol. 2012 Aug;20(8):392-401. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2012.04.008. Epub 2012 May 23. Trends Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22633075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human cytomegalovirus decathlon: Ten critical replication events provide opportunities for restriction.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 25;10:1053139. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1053139. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36506089 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alwine, J. C. 2008. Modulation of host cell stress responses by human cytomegalovirus, p. 263-279. In T. E. Shenk and M. F. Stinski (ed.), Current topics in microbiology and immunology, vol. 325. Human cytomegalovirus. Springer, New York, NY. - PubMed
-
- Antonsson, A., and P. J. H. Johansson. 2001. Binding of human and animal immunoglobulins to the IgG Fc receptor induced by human cytomegalovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 82:1137-1145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

