Spatial organization of genes as a component of regulated expression
- PMID: 19727792
- PMCID: PMC2809799
- DOI: 10.1007/s00412-009-0236-2
Spatial organization of genes as a component of regulated expression
Abstract
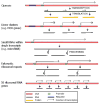
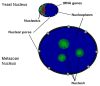
The DNA of living cells is highly compacted. Inherent in this spatial constraint is the need for cells to organize individual genetic loci so as to facilitate orderly retrieval of information. Complex genetic regulatory mechanisms are crucial to all organisms, and it is becoming increasingly evident that spatial organization of genes is one very important mode of regulation for many groups of genes. In eukaryotic nuclei, it appears not only that DNA is organized in three-dimensional space but also that this organization is dynamic and interactive with the transcriptional state of the genes. Spatial organization occurs throughout evolution and with genes transcribed by all classes of RNA polymerases in all eukaryotic nuclei, from yeast to human. There is an increasing body of work examining the ways in which this organization and consequent regulation are accomplished. In this review, we discuss the diverse strategies that cells use to preferentially localize various classes of genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Role of chromatin conformation in eukaryotic gene regulation].Yi Chuan. 2011 Dec;33(12):1291-9. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2011.01291. Yi Chuan. 2011. PMID: 22207374 Chinese.
-
Genetic and epigenetic control of the spatial organization of the genome.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Feb 1;28(3):364-369. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-03-0149. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28137949 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal RNA genes in eukaryotic microorganisms: witnesses of phylogeny?FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010 Jan;34(1):59-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00196.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 19930463 Review.
-
Spatial organization of transcribed eukaryotic genes.Nat Cell Biol. 2022 Mar;24(3):327-339. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-00847-6. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Nat Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35177821 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Positioning Effects on Expression in Eukaryotes.Annu Rev Genet. 2015;49:627-46. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-112414-055008. Epub 2015 Oct 2. Annu Rev Genet. 2015. PMID: 26436457 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromosome domain architecture and dynamic organization of the fission yeast genome.FEBS Lett. 2015 Oct 7;589(20 Pt A):2975-86. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Jun 19. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 26096785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neighbourhood continuity is not required for correct testis gene expression in Drosophila.PLoS Biol. 2010 Nov 30;8(11):e1000552. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000552. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 21151342 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-Level Assembly of the Caenorhabditis remanei Genome Reveals Conserved Patterns of Nematode Genome Organization.Genetics. 2020 Apr;214(4):769-780. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.303018. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Genetics. 2020. PMID: 32111628 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the DYRK1A gene correlates with its 3D positioning in the interphase nucleus of Down syndrome cells.Chromosome Res. 2015 Jun;23(2):285-98. doi: 10.1007/s10577-015-9467-7. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Chromosome Res. 2015. PMID: 25645734
-
Nuclear colocalization of transcription factor target genes strengthens coregulation in yeast.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(1):27-36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr689. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 21880591 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed S, Brickner JH. Regulation and epigenetic control of transcription at the nuclear periphery. Trends Genet. 2007;23:396–402. - PubMed
-
- Akam M. Hox and HOM: homologous gene clusters in insects and vertebrates. Cell. 1989;57:347–349. - PubMed
-
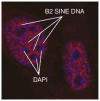
- Allen TA, Von Kaenel S, Goodrich JA, Kugel JF. The SINE-encoded mouse B2 RNA represses mRNA transcription in response to heat shock. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004;11:816–821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

