Interplay between Akt and p38 MAPK pathways in the regulation of renal tubular cell apoptosis associated with diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 19726550
- PMCID: PMC2806120
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00032.2009
Interplay between Akt and p38 MAPK pathways in the regulation of renal tubular cell apoptosis associated with diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
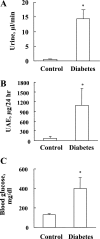
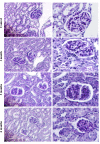
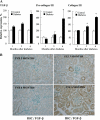
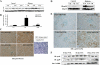
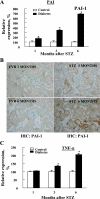
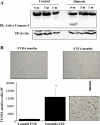
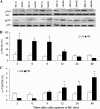
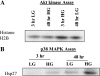
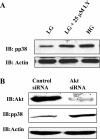
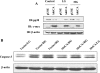
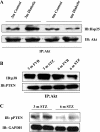
Hyperglycemia induces p38 MAPK-mediated renal proximal tubular cell (RPTC) apoptosis. The current study hypothesized that alteration of the Akt signaling pathway by hyperglycemia may contribute to p38 MAPK activation and development of diabetic nephropathy. Immunoblot analysis demonstrated a hyperglycemia-induced increase in Akt phosphorylation in diabetic kidneys at 1 mo, peaking at 3 mo, and dropping back to baseline by 6 mo. Immunohistochemical staining with anti-pAkt antisera localized Akt phosphorylation to renal tubules. Maximal p38 MAPK phosphorylation was detected concomitant with increase in terminal uridine deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL)-positive cells and caspase-3 activity in 6-mo diabetic kidneys. Exposure of cultured RPTCs to high glucose (HG; 22.5 mM) significantly increased Akt phosphorylation at 3, 6, and 9 h, and decreased thereafter. In contrast, p38 MAPK phosphorylation was detected between 9 and 48 h of HG treatment. Increased p38 MAPK activation at 24 and 48 h coincided with increased apoptosis, demonstrated by increased caspase-3 activity at 24 h and increased TUNEL-positive cells at 48 h of HG exposure. Blockade of p38 cascade with SB203850 inhibited HG-induced caspase-3 activation and TUNEL-positive cells. Overexpression of constitutively active Akt abrogated HG-induced p38 MAPK phosphorylation and RPTC apoptosis. In addition, blockade of the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway with LY294002 and silencing of Akt expression with Akt small interfering RNA induced p38 MAPK phosphorylation in the absence of HG. These results collectively suggest that downregulation of Akt activation during long-term hyperglycemia contributes to enhanced p38 MAPK activation and RPTC apoptosis. Mechanism of downregulation of Akt activation in 6-mo streptozotocin diabetic kidneys was attributed to decreased Akt-heat shock protein (Hsp) 25, Akt-p38 interaction, and decreased PTEN activity. Thus PTEN or Hsp25 could serve as potential therapeutic targets to modulate Akt activation and control p38 MAPK-mediated diabetic complications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TXNIP deficiency mitigates podocyte apoptosis via restraining the activation of mTOR or p38 MAPK signaling in diabetic nephropathy.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Mar 15;388(2):111862. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111862. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 31982382
-
Reactive nitrogen species induced by hyperglycemia suppresses Akt signaling and triggers apoptosis by upregulating phosphatase PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10) in an LKB1-dependent manner.Circulation. 2007 Oct 2;116(14):1585-95. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.716498. Epub 2007 Sep 17. Circulation. 2007. Retraction in: Circulation. 2020 Oct 13;142(15):e239. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000919. PMID: 17875968 Retracted.
-
FR167653 inhibits fibronectin expression and apoptosis in diabetic glomeruli and in high-glucose-stimulated mesangial cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008 Aug;295(2):F595-604. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00624.2007. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18524857
-
The Role of PKC-MAPK Signalling Pathways in the Development of Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiovascular Complications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 2;23(15):8582. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158582. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinase B/Akt regulation in diabetic kidney disease.Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2011 Jan 1;3(1):98-104. doi: 10.2741/s135. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2011. PMID: 21196360 Review.
Cited by
-
Tribbles homolog 3 attenuates mammalian target of rapamycin complex-2 signaling and inflammation in the diabetic kidney.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Sep;25(9):2067-78. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013070811. Epub 2014 Mar 27. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24676635 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of Vitamin D in Renal Tubulopathies.Metabolites. 2020 Mar 19;10(3):115. doi: 10.3390/metabo10030115. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 32204545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Linking Empagliflozin to Renal Protection in the LLC-PK1 Model of Diabetic Nephropathy.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 20;10(11):2983. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112983. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36428551 Free PMC article.
-
Lycopene ameliorates renal function in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Jul 15;7(8):5008-15. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25197372 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow-derived c-kit positive stem cell administration protects against diabetes-induced nephropathy in a rat model by reversing PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Mar;479(3):603-615. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04750-y. Epub 2023 May 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37129768
References
-
- Adhikary L, Chow F, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Stambe C, Dowling J, Atkins RC, Tesch GH. Abnormal p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling in human and experimental diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia 47: 1210–1222, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Allen DA, Harwood S, Varagunam M, Raftery MJ, Yaqoob MM. High glucose-induced oxidative stress causes apoptosis in proximal tubular epithelial cells and is mediated by multiple caspases. FASEB J 17: 908–910, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Birle D, Bottini N, Williams S, Huynh H, deBelle I, Adamson E, Mustelin T. Negative feedback regulation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by phosphoinositide-induced serine phosphorylation. J Immunol 169: 286–291, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Cai L, Li W, Wang G, Guo L, Jiang Y, Kang YJ. Hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in mouse myocardium: mitochondrial cytochrome C-mediated caspase-3 activation pathway. Diabetes 51: 1938–1948, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Cai L, Wang J, Li Y, Sun X, Wang L, Zhou Z, Kang YJ. Inhibition of superoxide generation and associated nitrosative damage is involved in metallothionein prevention of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes 54: 1829–1837, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

