Plexin D1 is ubiquitously expressed on tumor vessels and tumor cells in solid malignancies
- PMID: 19703316
- PMCID: PMC2739226
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-297
Plexin D1 is ubiquitously expressed on tumor vessels and tumor cells in solid malignancies
Abstract
Background: Plexin D1 is expressed on both tumor-associated endothelium and malignant cells in a number of clinical brain tumors. Recently we demonstrated that Plexin D1 expression is correlated with tumor invasion level and metastasis in a human melanoma progression series. The objective of this study was to examine whether Plexin D1 might be clinically useful as a pan-tumor vessel and pan-tumor cell target in solid tumors.
Methods: We examined Plexin D1 expression in clinical solid tumors (n = 77) of different origin, a selection of pre-malignant lesions (n = 29) and a variety of non-tumor related tissues (n = 52) by immunohistochemistry. Signals were verified in a selection of tissues via mRNA in situ hybridization.
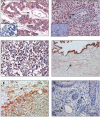
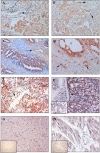
Results: Plexin D1 is abundantly expressed on both activated established tumor vasculature and malignant cells in the majority of primary and metastatic clinical tumors, as well as on macrophages and fibroblasts. Importantly, in non-tumor related tissues Plexin D1 expression is restricted to a subset of, presumably activated, fibroblasts and macrophages.
Conclusion: We demonstrate that Plexin D1 is in general ubiquitously expressed in tumor but not normal vasculature, as well as in malignant cells in a wide range of human tissues. This expression profile highlights Plexin D1 as a potentially valuable therapeutic target in clinical solid tumors, enabling simultaneous targeting of different tumor compartments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vascular Sema3E-Plexin-D1 Signaling Reactivation Promotes Post-stroke Recovery through VEGF Downregulation in Mice.Transl Stroke Res. 2022 Feb;13(1):142-159. doi: 10.1007/s12975-021-00914-4. Epub 2021 May 12. Transl Stroke Res. 2022. PMID: 33978913 Free PMC article.
-
Plexin-D1/Semaphorin 3E pathway may contribute to dysregulation of vascular tone control and defective angiogenesis in systemic sclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Aug 21;17(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0749-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26292963 Free PMC article.
-
Plexin D1 expression is induced on tumor vasculature and tumor cells: a novel target for diagnosis and therapy?Cancer Res. 2005 Sep 15;65(18):8317-23. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4366. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16166308
-
Divergent roles of Plexin D1 in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019 Aug;1872(1):103-110. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.05.004. Epub 2019 May 30. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31152824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the regulatory role of Plexin D1 signalling in cardiovascular development and diseases.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 May;25(9):4183-4194. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16509. Epub 2021 Apr 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33837646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Value of PLXND1 and TGF-β1 Coexpression and Its Correlation With Immune Infiltrates in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Jan 8;10:604131. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.604131. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33489909 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour growth inhibition and anti-metastatic activity of a mutated furin-resistant Semaphorin 3E isoform.EMBO Mol Med. 2012 Mar;4(3):234-50. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201100205. Epub 2012 Jan 13. EMBO Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22247010 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of talin in cancer progression and metastasis.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2011;289:117-47. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386039-2.00004-3. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21749900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse functions for the semaphorin receptor PlexinD1 in development and disease.Dev Biol. 2011 Jan 1;349(1):1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.09.008. Epub 2010 Sep 27. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 20880496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plexin D1 emerges as a novel target in the development of neural lineage plasticity in treatment-resistant prostate cancer.Oncogene. 2024 Jul;43(30):2325-2337. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03081-6. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38877132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendel DB, Laird AD, Xin X, Louie SG, Christensen JG, Li G, Schreck RE, Abrams TJ, Ngai TJ, Lee LB. In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors: determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:327–337. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7099–7109. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1443. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Presta LG, Chen H, O'Connor SJ, Chisholm V, Meng YG, Krummen L, Winkler M, Ferrara N. Humanization of an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monoclonal antibody for the therapy of solid tumors and other disorders. Cancer Res. 1997;57:4593–4599. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Pluzanska A, Koralewski P, Ravaud A, Bracarda S, Szczylik C, Chevreau C, Filipek M, Melichar B, Bajetta E. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet. 2007;370:2103–2111. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61904-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

