CBP-mediated acetylation of histone H3 lysine 27 antagonizes Drosophila Polycomb silencing
- PMID: 19700617
- PMCID: PMC2730368
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.037127
CBP-mediated acetylation of histone H3 lysine 27 antagonizes Drosophila Polycomb silencing
Abstract
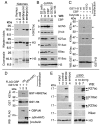
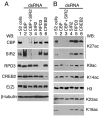
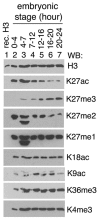
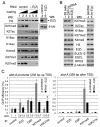
Trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3) by Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) is essential for transcriptional silencing of Polycomb target genes, whereas acetylation of H3K27 (H3K27ac) has recently been shown to be associated with many active mammalian genes. The Trithorax protein (TRX), which associates with the histone acetyltransferase CBP, is required for maintenance of transcriptionally active states and antagonizes Polycomb silencing, although the mechanism underlying this antagonism is unknown. Here we show that H3K27 is specifically acetylated by Drosophila CBP and its deacetylation involves RPD3. H3K27ac is present at high levels in early embryos and declines after 4 hours as H3K27me3 increases. Knockdown of E(Z) decreases H3K27me3 and increases H3K27ac in bulk histones and at the promoter of the repressed Polycomb target gene abd-A, suggesting that these indeed constitute alternative modifications at some H3K27 sites. Moderate overexpression of CBP in vivo causes a global increase in H3K27ac and a decrease in H3K27me3, and strongly enhances Polycomb mutant phenotypes. We also show that TRX is required for H3K27 acetylation. TRX overexpression also causes an increase in H3K27ac and a concomitant decrease in H3K27me3 and leads to defects in Polycomb silencing. Chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with DNA microarray (ChIP-chip) analysis reveals that H3K27ac and H3K27me3 are mutually exclusive and that H3K27ac and H3K4me3 signals coincide at most sites. We propose that TRX-dependent acetylation of H3K27 by CBP prevents H3K27me3 at Polycomb target genes and constitutes a key part of the molecular mechanism by which TRX antagonizes or prevents Polycomb silencing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A mutation in the E(Z) methyltransferase that increases trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 27 and causes inappropriate silencing of active Polycomb target genes.Dev Biol. 2012 Apr 15;364(2):249-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.12.007. Epub 2011 Dec 11. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22182520
-
Histone demethylase UTX and chromatin remodeler BRM bind directly to CBP and modulate acetylation of histone H3 lysine 27.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jun;32(12):2323-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06392-11. Epub 2012 Apr 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22493065 Free PMC article.
-
Trithorax monomethylates histone H3K4 and interacts directly with CBP to promote H3K27 acetylation and antagonize Polycomb silencing.Development. 2014 Mar;141(5):1129-39. doi: 10.1242/dev.102392. Development. 2014. PMID: 24550119 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic occupancy of the transcriptional co-activators p300 and CBP.Transcription. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):18-23. doi: 10.4161/trns.22601. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Transcription. 2013. PMID: 23131664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation in plant development.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2011 Apr;14(2):123-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2011.01.001. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2011. PMID: 21330185 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic factor competition reshapes the EMT landscape.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 18;119(42):e2210844119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2210844119. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36215492 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide recruitment to Polycomb-modified chromatin and activity regulation of the synovial sarcoma oncogene SYT-SSX2.BMC Genomics. 2012 May 17;13:189. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-189. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22594313 Free PMC article.
-
STAT1 epigenetically regulates LCP2 and TNFAIP2 by recruiting EP300 to contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease.Clin Epigenetics. 2021 Jun 10;13(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01101-w. Clin Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 34112215 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancer dependence of cell-type-specific gene expression increases with developmental age.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 1;117(35):21450-21458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008672117. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32817427 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of epigenetic features characteristic of L1 loci expressed in human cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Feb 28;50(4):1888-1907. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35100410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agger, K., Cloos, P. A., Christensen, J., Pasini, D., Rose, S., Rappsilber, J., Issaeva, I., Canaani, E., Salcini, A. E. and Helin, K. (2007). UTX and JMJD3 are histone H3K27 demethylases involved in HOX gene regulation and development. Nature 449, 731-734. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad, K. and Henikoff, S. (2002). The histone variant H3.3 marks active chromatin by replication-independent nucleosome assembly. Mol. Cell 9, 1191-1200. - PubMed
-
- Akimaru, H., Chen, Y., Dai, P., Hou, D. X., Nonaka, M., Smolik, S. M., Armstrong, S., Goodman, R. H. and Ishii, S. (1997). Drosophila CBP is a co-activator of cubitus interruptus in hedgehog signalling. Nature 386, 735-738. - PubMed
-
- Barski, A., Cuddapah, S., Cui, K., Roh, T. Y., Schones, D. E., Wang, Z., Wei, G., Chepelev, I. and Zhao, K. (2007). High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 129, 823-837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

