A molecular basis for phosphorylation-dependent SUMO conjugation by the E2 UBC9
- PMID: 19684601
- PMCID: PMC2771680
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1648
A molecular basis for phosphorylation-dependent SUMO conjugation by the E2 UBC9
Abstract
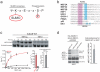
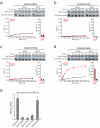
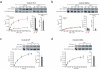
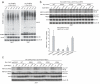
Phosphorylation and small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) conjugation contribute to the spatial and temporal regulation of substrates containing phosphorylation-dependent SUMO consensus motifs (PDSMs). Myocyte-enhancement factor 2 (MEF2) is a transcription factor and PDSM substrate whose modification by SUMO drives postsynaptic dendritic differentiation. NMR analysis revealed that the human SUMO E2 interacted with model substrates for phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated MEF2 in similar extended conformations. Mutational and biochemical analysis identified a basic E2 surface that enhanced SUMO conjugation to phosphorylated PDSM substrates MEF2 and heat-shock transcription factor 1 (HSF1), but not to nonphosphorylated MEF2 or HSF1, nor the non-PDSM substrate p53. Mutant ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBC9 isoforms defective in promoting SUMO conjugation to phosphorylated MEF2 in vitro and in vivo also impair postsynaptic differentiation in organotypic cerebellar slices. These data support an E2-dependent mechanism that underlies phosphorylation-dependent SUMO conjugation in pathways that range from the heat-shock response to nuclear hormone signaling to brain development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unique binding interactions among Ubc9, SUMO and RanBP2 reveal a mechanism for SUMO paralog selection.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005 Jan;12(1):67-74. doi: 10.1038/nsmb878. Epub 2004 Dec 19. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15608651
-
Solution structure of human SUMO-3 C47S and its binding surface for Ubc9.Biochemistry. 2005 Mar 1;44(8):2790-9. doi: 10.1021/bi0477586. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15723523
-
Site-specific inhibition of the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO)-conjugating enzyme Ubc9 selectively impairs SUMO chain formation.J Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 15;292(37):15340-15351. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.794255. Epub 2017 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28784659 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO: getting it on.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Dec;35(Pt 6):1409-13. doi: 10.1042/BST0351409. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 18031233 Review.
-
Purification of SUMO conjugating enzymes and kinetic analysis of substrate conjugation.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;497:167-86. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-566-4_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19107417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SUMO targets the APC/C to regulate transition from metaphase to anaphase.Nat Commun. 2018 Mar 16;9(1):1119. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03486-4. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29549242 Free PMC article.
-
Entropy-driven mechanism of an E3 ligase.Biochemistry. 2011 Jun 28;50(25):5757-66. doi: 10.1021/bi2001856. Epub 2011 Jun 3. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21568279 Free PMC article.
-
Sumoylation of Krüppel-like factor 4 inhibits pluripotency induction but promotes adipocyte differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 3;288(18):12791-804. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.465443. Epub 2013 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23515309 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like signaling networks.Chem Rev. 2011 Dec 14;111(12):7923-40. doi: 10.1021/cr200187e. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Chem Rev. 2011. PMID: 22004258 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Sumoylation in gene regulation, human disease, and therapeutic action.F1000Prime Rep. 2013 Nov 1;5:45. doi: 10.12703/P5-45. eCollection 2013. F1000Prime Rep. 2013. PMID: 24273646 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Johnson ES. Protein modification by SUMO. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004;73:355–382. - PubMed
-
- Geiss-Freidlander R, Melchior F. Concepts in sumoylation: a decade on. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:947–56. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Dye BT, Schulman BA. Structural mechanism underlying posttranslational modification by ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2007;36:131–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

