Direct activation of protein kinases by unanchored polyubiquitin chains
- PMID: 19675569
- PMCID: PMC2747300
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08247
Direct activation of protein kinases by unanchored polyubiquitin chains
Abstract
TRAF6 is a ubiquitin ligase that is essential for the activation of NF-kappaB and MAP kinases in several signalling pathways, including those emanating from the interleukin 1 and Toll-like receptors. TRAF6 functions together with a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex consisting of UBC13 (also known as UBE2N) and UEV1A (UBE2V1) to catalyse Lys 63-linked polyubiquitination, which activates the TAK1 (also known as MAP3K7) kinase complex. TAK1 in turn phosphorylates and activates IkappaB kinase (IKK), leading to the activation of NF-kappaB. Although several proteins are known to be polyubiquitinated in the IL1R and Toll-like receptor pathways, it is not clear whether ubiquitination of any of these proteins is important for TAK1 or IKK activation. By reconstituting TAK1 activation in vitro using purified proteins, here we show that free Lys 63 polyubiquitin chains, which are not conjugated to any target protein, directly activate TAK1 by binding to the ubiquitin receptor TAB2 (also known as MAP3K7IP2). This binding leads to autophosphorylation and activation of TAK1. Furthermore, we found that unanchored polyubiquitin chains synthesized by TRAF6 and UBCH5C (also known as UBE2D3) activate the IKK complex. Disassembly of the polyubiquitin chains by deubiquitination enzymes prevented TAK1 and IKK activation. These results indicate that unanchored polyubiquitin chains directly activate TAK1 and IKK, suggesting a new mechanism of protein kinase regulation.
Figures
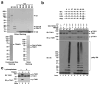
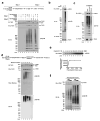
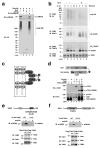
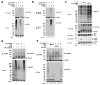
Similar articles
-
TAK1 is a ubiquitin-dependent kinase of MKK and IKK.Nature. 2001 Jul 19;412(6844):346-51. doi: 10.1038/35085597. Nature. 2001. PMID: 11460167
-
TAB2 and TAB3 activate the NF-kappaB pathway through binding to polyubiquitin chains.Mol Cell. 2004 Aug 27;15(4):535-48. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.08.008. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15327770
-
ATM- and NEMO-dependent ELKS ubiquitination coordinates TAK1-mediated IKK activation in response to genotoxic stress.Mol Cell. 2010 Oct 8;40(1):75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.010. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20932476 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-mediated activation of TAK1 and IKK.Oncogene. 2007 May 14;26(22):3214-26. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210413. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17496917 Review.
-
Ubiquitination in signaling to and activation of IKK.Immunol Rev. 2012 Mar;246(1):95-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01108.x. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22435549 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Capsids to Complexes: Expanding the Role of TRIM5α in the Restriction of Divergent RNA Viruses and Elements.Viruses. 2021 Mar 10;13(3):446. doi: 10.3390/v13030446. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33801908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and characterization of a novel ISG15-ubiquitin mixed chain and its role in regulating protein homeostasis.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 30;5:12704. doi: 10.1038/srep12704. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26226047 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB activation: Tax sumoylation is out, but what about Tax ubiquitination?Retrovirology. 2012 Sep 25;9:78. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-9-78. Retrovirology. 2012. PMID: 23009565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peli: a family of signal-responsive E3 ubiquitin ligases mediating TLR signaling and T-cell tolerance.Cell Mol Immunol. 2012 Mar;9(2):113-22. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2011.60. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Cell Mol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22307041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serine/threonine acetylation of TGFβ-activated kinase (TAK1) by Yersinia pestis YopJ inhibits innate immune signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 31;109(31):12710-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008203109. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22802624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inoue J, Gohda J, Akiyama T. Characteristics and biological functions of TRAF6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;597:72–79. - PubMed
-
- Wang C, et al. TAK1 is a ubiquitin-dependent kinase of MKK and IKK. Nature. 2001;412:346–351. - PubMed
-
- Deng L, et al. Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex by TRAF6 requires a dimeric ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex and a unique polyubiquitin chain. Cell. 2000;103:351–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

