Extracellular matrix genes as hypoxia-inducible targets
- PMID: 19662436
- PMCID: PMC3074490
- DOI: 10.1007/s00441-009-0841-7
Extracellular matrix genes as hypoxia-inducible targets
Abstract
Low oxygen tension, i.e., hypoxia, is a pathophysiological component involved in many human disorders but is also a critically important phenomenon in normal development and differentiation. The ability of cells to survive under hypoxia or to adapt to it depends on a family of hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIFs) that induce the expression of a number of genes involved in hematopoiesis, angiogenesis, iron transport, glucose utilization, resistance to oxidative stress, cell proliferation, survival and apoptosis, and extracellular matrix homeostasis. We introduce here the recently identified molecular mechanisms responsible for the oxygen-dependent stability and activity of HIF, after which we focus on extracellular matrix genes as HIF targets. The vital role of the hypoxia response pathway in chondrogenesis and joint development is then discussed.
Figures


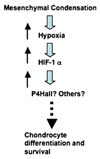
Similar articles
-
Effects of exposure to a DNA damaging agent on the hypoxia inducible factors in organogenesis stage mouse limbs.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51937. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051937. Epub 2012 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251655 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl 4-hydroxylases: common and specific roles.Biol Chem. 2013 Apr;394(4):435-48. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0328. Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23324380 Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 3 biology: complexities and emerging themes.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Feb 15;310(4):C260-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00315.2015. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26561641 Review.
-
Flavonoid Compound Icariin Activates Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α in Chondrocytes and Promotes Articular Cartilage Repair.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 3;11(2):e0148372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148372. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26841115 Free PMC article.
-
The HIF pathway: implications for patterns of gene expression in cancer.Novartis Found Symp. 2001;240:212-25; discussion 225-31. doi: 10.1002/0470868716.ch15. Novartis Found Symp. 2001. PMID: 11727931 Review.
Cited by
-
Physiological ROS controls Upd3-dependent modeling of ECM to support cardiac function in Drosophila.Sci Adv. 2022 Feb 18;8(7):eabj4991. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abj4991. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35179958 Free PMC article.
-
Roxadustat Attenuates Adverse Remodeling Following Myocardial Infarction in Mice.Cells. 2024 Jun 21;13(13):1074. doi: 10.3390/cells13131074. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994928 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen Remodeling in the Hypoxic Tumor-Mesothelial Niche Promotes Ovarian Cancer Metastasis.Cancer Res. 2019 May 1;79(9):2271-2284. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2616. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30862717 Free PMC article.
-
Redox-relevant aspects of the extracellular matrix and its cellular contacts via integrins.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 May 1;20(13):1977-93. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5294. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24040997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of hypoxia inducible factor HIF-1α in heart valves.Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2023 May 11;2023(2):e202309. doi: 10.21542/gcsp.2023.9. eCollection 2023 May 11. Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2023. PMID: 37351095 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amarilio R, Viukov SV, Sharir A, Eshkar-Oren I, Johnson RS, Zelzer E. HIF1α regulation of Sox9 is necessary to maintain differentiation of hypoxic prechondrogenic cells during early skeletogenesis. Development. 2007;134:3917–3928. - PubMed
-
- Berg JT, Breen EC, Fu Z, Mathieu-Costello O, West JB. Alveolar hypoxia increases gene expression of extracellular matrix proteins and platelet-derived growth factor-B in lung parenchyma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;158:1921–1928. - PubMed
-
- tenBerge D, Brouwer A, Korving J, Martin JF, Meijlink F. Prx1 and Prx2 in skeletogenesis: roles in the craniofacial region, inner ear and limbs. Development. 1998;125:3831–3842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

