Effect of B-cell depletion on viral replication and clinical outcome of simian immunodeficiency virus infection in a natural host
- PMID: 19656874
- PMCID: PMC2753117
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00880-09
Effect of B-cell depletion on viral replication and clinical outcome of simian immunodeficiency virus infection in a natural host
Abstract
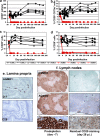
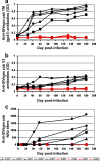
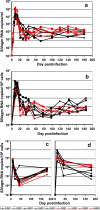
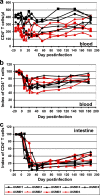
Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-infected African nonhuman primates do not progress to AIDS in spite of high and persistent viral loads (VLs). Some authors consider the high viral replication observed in chronic natural SIV infections to be due to lower anti-SIV antibody titers than those in rhesus macaques, suggesting a role of antibodies in controlling viral replication. We therefore investigated the impact of antibody responses on the outcome of acute and chronic SIVagm replication in African green monkeys (AGMs). Nine AGMs were infected with SIVagm.sab. Four AGMs were infused with 50 mg/kg of body weight anti-CD20 (rituximab; a gift from Genentech) every 21 days, starting from day -7 postinfection up to 184 days. The remaining AGMs were used as controls and received SIVagm only. Rituximab-treated AGMs were successfully depleted of CD20 cells in peripheral blood, lymph nodes (LNs), and intestine, as shown by the dynamics of CD20+ and CD79a+ cells. There was no significant difference in VLs between CD20-depleted AGMs and control monkeys: peak VLs ranged from 10(7) to 10(8) copies/ml; set-point values were 10(4) to 10(5) SIV RNA copies/ml. Levels of acute mucosal CD4+ T-cell depletion were similar for treated and nontreated animals. SIVagm seroconversion was delayed for the CD20-depleted AGMs compared to results for the controls. There was a significant difference in both the timing and magnitude of neutralizing antibody responses for CD20-depleted AGMs compared to results for controls. CD20 depletion significantly altered the histological structure of the germinal centers in the LNs and Peyer's patches. Our results, although obtained with a limited number of animals, suggest that humoral immune responses play only a minor role in the control of SIV viral replication during acute and chronic SIV infection in natural hosts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experimental depletion of CD8+ cells in acutely SIVagm-infected African Green Monkeys results in increased viral replication.Retrovirology. 2010 May 11;7:42. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-7-42. Retrovirology. 2010. PMID: 20459829 Free PMC article.
-
Simian immunodeficiency virus SIVagm.sab infection of Caribbean African green monkeys: a new model for the study of SIV pathogenesis in natural hosts.J Virol. 2006 May;80(10):4858-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.10.4858-4867.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16641277 Free PMC article.
-
Limited ability of humoral immune responses in control of viremia during infection with SIVsmmD215 strain.Blood. 2009 Apr 30;113(18):4250-61. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-09-177741. Epub 2009 Jan 23. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19168789 Free PMC article.
-
SIVagm: genetic and biological features associated with replication.Front Biosci. 2003 Sep 1;8:d1170-85. doi: 10.2741/1130. Front Biosci. 2003. PMID: 12957815 Review.
-
What can natural infection of African monkeys with simian immunodeficiency virus tell us about the pathogenesis of AIDS?AIDS Rev. 2004 Jan-Mar;6(1):40-53. AIDS Rev. 2004. PMID: 15168740 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial Translocation and B Cell Dysfunction in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Disease.Am J Immunol. 2012;8(2):44-51. doi: 10.3844/ajisp.2012.44.51. Am J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23869197 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Development of gp120-Focused Neutralizing B Cell Responses during Acute Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection of African Green Monkeys.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(18):9485-98. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01564-15. Epub 2015 Jul 8. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26157116 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic features associated with increased virulence upon Simian immunodeficiency virus cross-species transmission from natural hosts.J Virol. 2014 Jun;88(12):6778-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03785-13. Epub 2014 Apr 2. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24696477 Free PMC article.
-
Non-neutralizing Antibodies May Contribute to Suppression of SIVmac239 Viremia in Indian Rhesus Macaques.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 16;12:657424. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.657424. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33796119 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic identity and biological phenotype of a transmitted/founder virus representative of nonpathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus infection in African green monkeys.J Virol. 2010 Dec;84(23):12245-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01603-10. Epub 2010 Sep 29. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20881048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan, J. S., J. Strauss, and D. W. Buck. 1990. Enhancement of SIV infection with soluble receptor molecules. Science 247:1084-1088. - PubMed
-
- Anolik, J. H., D. Campbell, R. E. Felgar, F. Young, I. Sanz, J. Rosenblatt, and R. J. Looney. 2003. The relationship of FcγRIIIa genotype to degree of B cell depletion by rituximab in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 48:455-459. - PubMed
-
- Barry, A. P., G. Silvestri, J. T. Safrit, B. Sumpter, N. Kozyr, H. M. McClure, S. I. Staprans, and M. B. Feinberg. 2007. Depletion of CD8+ cells in sooty mangabey monkeys naturally infected with simian immunodeficiency virus reveals limited role for immune control of virus replication in a natural host species. J. Immunol. 178:8002-8012. - PubMed
-
- Brenchley, J. M., D. A. Price, T. W. Schacker, T. E. Asher, G. Silvestri, S. Rao, Z. Kazzaz, O. Lambotte, D. Altmann, B. R. Blazar, B. Rodriguez, L. Teixeira-Johnson, A. Landay, J. N. Martin, F. M. Hecht, L. J. Picker, M. Lederman, S. G. Deeks, and D. C. Douek. 2006. Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat. Med. 12:1365-1371. - PubMed
-
- Cartron, G., L. Dacheux, G. Salles, P. Solal-Celigny, P. Bardos, P. Colombat, and H. Watier. 2002. Therapeutic activity of humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and polymorphism in IgG Fc receptor FcγRIIIa gene. Blood 99:754-758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

