Hox specificity unique roles for cofactors and collaborators
- PMID: 19651302
- PMCID: PMC2810641
- DOI: 10.1016/S0070-2153(09)88003-4
Hox specificity unique roles for cofactors and collaborators
Abstract
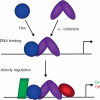
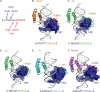
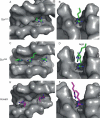
Hox proteins are well known for executing highly specific functions in vivo, but our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying gene regulation by these fascinating proteins has lagged behind. The premise of this review is that an understanding of gene regulation-by any transcription factor-requires the dissection of the cis-regulatory elements that they act upon. With this goal in mind, we review the concepts and ideas regarding gene regulation by Hox proteins and apply them to a curated list of directly regulated Hox cis-regulatory elements that have been validated in the literature. Our analysis of the Hox-binding sites within these elements suggests several emerging generalizations. We distinguish between Hox cofactors, proteins that bind DNA cooperatively with Hox proteins and thereby help with DNA-binding site selection, and Hox collaborators, proteins that bind in parallel to Hox-targeted cis-regulatory elements and dictate the sign and strength of gene regulation. Finally, we summarize insights that come from examining five X-ray crystal structures of Hox-cofactor-DNA complexes. Together, these analyses reveal an enormous amount of flexibility into how Hox proteins function to regulate gene expression, perhaps providing an explanation for why these factors have been central players in the evolution of morphological diversity in the animal kingdom.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vivo Hox binding specificity revealed by systematic changes to a single cis regulatory module.Nat Commun. 2019 Aug 9;10(1):3597. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11416-1. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31399572 Free PMC article.
-
A structural model for a homeotic protein-extradenticle-DNA complex accounts for the choice of HOX protein in the heterodimer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 28;93(11):5223-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.11.5223. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8643557 Free PMC article.
-
Activity regulation of a Hox protein and a role for the homeodomain in inhibiting transcriptional activation.EMBO J. 1999 Jan 4;18(1):198-211. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.1.198. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 9878063 Free PMC article.
-
To Be Specific or Not: The Critical Relationship Between Hox And TALE Proteins.Trends Genet. 2016 Jun;32(6):334-347. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Trends Genet. 2016. PMID: 27066866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shaping segments: Hox gene function in the genomic age.Bioessays. 2008 Oct;30(10):965-79. doi: 10.1002/bies.20823. Bioessays. 2008. PMID: 18798525 Review.
Cited by
-
'Organ'ising Floral Organ Development.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 8;13(12):1595. doi: 10.3390/plants13121595. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of an abdominal Hox complex with Pax2 yields cell-specific EGF secretion from Drosophila sensory precursor cells.Development. 2012 May;139(9):1611-9. doi: 10.1242/dev.077842. Epub 2012 Mar 21. Development. 2012. PMID: 22438572 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-step control of muscle diversity by Hox proteins in the Drosophila embryo.Development. 2010 Feb;137(3):457-66. doi: 10.1242/dev.045286. Epub 2010 Jan 7. Development. 2010. PMID: 20056681 Free PMC article.
-
Hox proteins interact to pattern neuronal subtypes in Caenorhabditis elegans males.Genetics. 2022 Apr 4;220(4):iyac010. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac010. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35137058 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of a versatile BiFC ORFeome library for analyzing protein-protein interactions in live Drosophila.Elife. 2018 Sep 24;7:e38853. doi: 10.7554/eLife.38853. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30247122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Affolter M, Slattery M, Mann RS. A lexicon for homeodomain-DNA recognition. Cell. 2008;133:1133–1135. - PubMed
-
- Akam M. Hox and HOM: homologous gene clusters in insects and vertebrates. Cell. 1989;57:347–349. - PubMed
-
- Arata Y, Kouike H, Zhang Y, Herman MA, Okano H, Sawa H. Wnt signaling and a Hox protein cooperatively regulate psa-3/Meis to determine daughter cell fate after asymmetric cell division in C. elegans. Dev. Cell. 2006;11:105–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

