Inhibition of heterotrimeric G protein signaling by a small molecule acting on Galpha subunit
- PMID: 19648112
- PMCID: PMC2781458
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.042333
Inhibition of heterotrimeric G protein signaling by a small molecule acting on Galpha subunit
Abstract
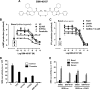
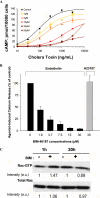
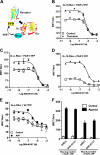
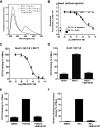
The simultaneous activation of many distinct G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and heterotrimeric G proteins play a major role in various pathological conditions. Pan-inhibition of GPCR signaling by small molecules thus represents a novel strategy to treat various diseases. To better understand such therapeutic approach, we have characterized the biomolecular target of BIM-46187, a small molecule pan-inhibitor of GPCR signaling. Combining bioluminescence and fluorescence resonance energy transfer techniques in living cells as well as in reconstituted receptor-G protein complexes, we observed that, by direct binding to the Galpha subunit, BIM-46187 prevents the conformational changes of the receptor-G protein complex associated with GPCR activation. Such a binding prevents the proper interaction of receptors with the G protein heterotrimer and inhibits the agonist-promoted GDP/GTP exchange. These observations bring further evidence that inhibiting G protein activation through direct binding to the Galpha subunit is feasible and should constitute a new strategy for therapeutic intervention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anticancer activity of BIM-46174, a new inhibitor of the heterotrimeric Galpha/Gbetagamma protein complex.Cancer Res. 2006 Sep 15;66(18):9227-34. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4205. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16982767
-
Signaling through G protein coupled receptors.Plant Signal Behav. 2009 Oct;4(10):942-7. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.10.9530. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Plant Signal Behav. 2009. PMID: 19826234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling from G protein-coupled receptors to ERK5/Big MAPK 1 involves Galpha q and Galpha 12/13 families of heterotrimeric G proteins. Evidence for the existence of a novel Ras AND Rho-independent pathway.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 14;275(28):21730-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002410200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10781600
-
Gγ and Gα Identity Dictate a G-Protein Heterotrimer Plasma Membrane Targeting.Cells. 2019 Oct 13;8(10):1246. doi: 10.3390/cells8101246. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31614907 Free PMC article.
-
Research Advances in Heterotrimeric G-Protein α Subunits and Uncanonical G-Protein Coupled Receptors in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 12;22(16):8678. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168678. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445383 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A cell-permeable inhibitor to trap Gαq proteins in the empty pocket conformation.Chem Biol. 2014 Jul 17;21(7):890-902. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.06.003. Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 25036778 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical and chemical activation of GPR68 probed with a genetically encoded fluorescent reporter.J Cell Sci. 2021 Aug 15;134(16):jcs255455. doi: 10.1242/jcs.255455. Epub 2021 Aug 17. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 34322699 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-sensing receptors signal constitutive macropinocytosis and facilitate the uptake of NOD2 ligands in macrophages.Nat Commun. 2016 Apr 6;7:11284. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11284. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27050483 Free PMC article.
-
Druggable Targets in Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling Pathways in Apicomplexan Parasites and Kinetoplastids against Disabling Protozoan Diseases in Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 2;20(1):138. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010138. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30609697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LPA1-mediated inhibition of CXCR4 attenuates CXCL12-induced signaling and cell migration.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 25;21(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01261-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37749552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lundstrom K. (2006) Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 7, 465–470 - PubMed
-
- Overington J. P., Al-Lazikani B., Hopkins A. L. (2006) Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 5, 993–996 - PubMed
-
- Dorsam R. T., Gutkind J. S. (2007) Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 79–94 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S., Dray A. (2004) Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 5, 67–70 - PubMed
-
- Cotecchia S., Fanelli F., Costa T. (2003) Assay. Drug Dev. Technol. 1, 311–316 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

