Human cytomegalovirus exploits ESCRT machinery in the process of virion maturation
- PMID: 19640981
- PMCID: PMC2753131
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01093-09
Human cytomegalovirus exploits ESCRT machinery in the process of virion maturation
Abstract
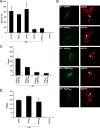
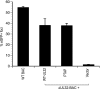
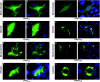
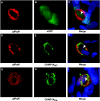
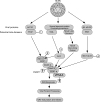
The endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) machinery controls the incorporation of cargo into intraluminal vesicles of multivesicular bodies. This machinery is used during envelopment of many RNA viruses and some DNA viruses, including herpes simplex virus type 1. Other viruses mature independent of ESCRT components, instead relying on the intrinsic behavior of viral matrix and envelope proteins to drive envelopment. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) maturation has been reported to proceed independent of ESCRT components (A. Fraile-Ramos et al. Cell. Microbiol. 9:2955-2967, 2007). A virus complementation assay was used to evaluate the role of dominant-negative (DN) form of a key ESCRT ATPase, vacuolar protein sorting-4 (Vps4DN) in HCMV replication. Vps4DN specifically inhibited viral replication, whereas wild-type-Vps4 had no effect. In addition, a DN form of charged multivesicular body protein 1 (CHMP1DN) was found to inhibit HCMV. In contrast, DN tumor susceptibility gene-101 (Tsg101DN) did not impact viral replication despite the presence of a PTAP motif within pp150/ppUL32, an essential tegument protein involved in the last steps of viral maturation and release. Either Vps4DN or CHMP1DN blocked viral replication at a step after the accumulation of late viral proteins, suggesting that both are involved in maturation. Both Vps4A and CHMP1A localized in the vicinity of viral cytoplasmic assembly compartments, sites of viral maturation that develop in CMV-infected cells. Thus, ESCRT machinery is involved in the final steps of HCMV replication.
Figures
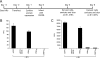
Similar articles
-
The ESCRT machinery is not required for human cytomegalovirus envelopment.Cell Microbiol. 2007 Dec;9(12):2955-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01024.x. Epub 2007 Aug 29. Cell Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17760879
-
Nonenvelopment Role for the ESCRT-III Complex during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection.J Virol. 2018 May 29;92(12):e02096-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02096-17. Print 2018 Jun 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29618648 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 production requires a functional ESCRT-III complex but is independent of TSG101 and ALIX expression.J Virol. 2009 Nov;83(21):11254-64. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00574-09. Epub 2009 Aug 19. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19692479 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of Endosomal Sorting Complex Required for Transport and accessory proteins in multivesicular body sorting and enveloped viral budding - An overview.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Apr 15;127:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.015. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30615963 Review.
-
Assembly and disassembly of the ESCRT-III membrane scission complex.FEBS Lett. 2011 Oct 20;585(20):3191-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.09.001. Epub 2011 Sep 9. FEBS Lett. 2011. PMID: 21924267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Why Cells and Viruses Cannot Survive without an ESCRT.Cells. 2021 Feb 24;10(3):483. doi: 10.3390/cells10030483. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33668191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus UL135 and UL136 Genes Are Required for Postentry Tropism in Endothelial Cells.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(13):6536-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00284-15. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25878111 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative membrane proteomics reveals a role for tetraspanin enriched microdomains during entry of human cytomegalovirus.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 9;12(11):e0187899. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187899. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29121670 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus deploys molecular mimicry to recruit VPS4A to sites of virus assembly.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jun 20;20(6):e1012300. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012300. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38900818 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay between ESCRT and Viral Factors in the Enveloped Virus Life Cycle.Viruses. 2021 Feb 20;13(2):324. doi: 10.3390/v13020324. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33672541 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Calistri, A., P. Sette, C. Salata, E. Cancellotti, C. Forghieri, A. Comin, H. Gottlinger, G. Campadelli-Fiume, G. Palu, and C. Parolin. 2007. Intracellular trafficking and maturation of herpes simplex virus type 1 gB and virus egress require functional biogenesis of multivesicular bodies. J. Virol. 81:11468-11478. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

