GABA(B) receptor activation inhibits neuronal excitability and spatial learning in the entorhinal cortex by activating TREK-2 K+ channels
- PMID: 19640481
- PMCID: PMC2735825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.06.022
GABA(B) receptor activation inhibits neuronal excitability and spatial learning in the entorhinal cortex by activating TREK-2 K+ channels
Abstract
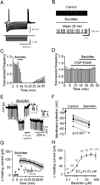
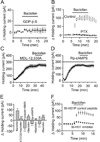
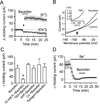
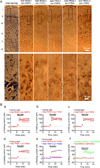
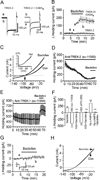
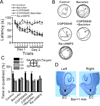
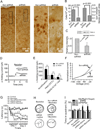
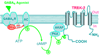
The entorhinal cortex (EC) is regarded as the gateway to the hippocampus and thus is essential for learning and memory. Whereas the EC expresses a high density of GABA(B) receptors, the functions of these receptors in this region remain unexplored. Here, we examined the effects of GABA(B) receptor activation on neuronal excitability in the EC and spatial learning. Application of baclofen, a specific GABA(B) receptor agonist, inhibited significantly neuronal excitability in the EC. GABA(B) receptor-mediated inhibition in the EC was mediated via activating TREK-2, a type of two-pore domain K(+) channels, and required the functions of inhibitory G proteins and protein kinase A pathway. Depression of neuronal excitability in the EC underlies GABA(B) receptor-mediated inhibition of spatial learning as assessed by Morris water maze. Our study indicates that GABA(B) receptors exert a tight control over spatial learning by modulating neuronal excitability in the EC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noradrenergic depression of neuronal excitability in the entorhinal cortex via activation of TREK-2 K+ channels.J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 17;284(16):10980-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806760200. Epub 2009 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19244246 Free PMC article.
-
Lamina-specific differences in GABA(B) autoreceptor-mediated regulation of spontaneous GABA release in rat entorhinal cortex.Neuropharmacology. 2004 Jan;46(1):31-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2003.07.001. Neuropharmacology. 2004. PMID: 14654095
-
Serotonin increases GABA release in rat entorhinal cortex by inhibiting interneuron TASK-3 K+ channels.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008 Oct;39(2):273-84. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2008.07.005. Epub 2008 Jul 18. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18687403 Free PMC article.
-
Kindling alters entorhinal cortex-hippocampal interaction by increased efficacy of presynaptic GABA(B) autoreceptors in layer III of the entorhinal cortex.Neurobiol Dis. 2003 Aug;13(3):203-12. doi: 10.1016/s0969-9961(03)00039-1. Neurobiol Dis. 2003. PMID: 12901834
-
Serotonin inhibits neuronal excitability by activating two-pore domain k+ channels in the entorhinal cortex.Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;72(1):208-18. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.034389. Epub 2007 Apr 23. Mol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17452494
Cited by
-
Behavioral characterization of mice lacking Trek channels.Front Behav Neurosci. 2012 Sep 7;6:60. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2012.00060. eCollection 2012. Front Behav Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22973213 Free PMC article.
-
Corticotropin-releasing factor facilitates epileptiform activity in the entorhinal cortex: roles of CRF2 receptors and PKA pathway.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 4;9(2):e88109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088109. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24505399 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviation by GABAB Receptors of Neurotoxicity Mediated by Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore in Cultured Murine Cortical Neurons Exposed to N-Methyl-D-aspartate.Neurochem Res. 2018 Jan;43(1):79-88. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2311-z. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 28608233
-
Multivariate analysis of subjective responses to d-amphetamine in healthy volunteers finds novel genetic pathway associations.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Aug;232(15):2781-94. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3914-1. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25843748 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of GABAB receptors in the insula bidirectionally affects associative memory of epilectic rats in both spatial and non-spatial operant tasks.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Jan 4;16:1042227. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1042227. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36688127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnsten AF, Ramos BP, Birnbaum SG, Taylor JR. Protein kinase A as a therapeutic target for memory disorders: rationale and challenges. Trends Mol Med. 2005;11:121–128. - PubMed
-
- Avoli M, D'Antuono M, Louvel J, Kohling R, Biagini G, Pumain R, D'Arcangelo G, Tancredi V. Network and pharmacological mechanisms leading to epileptiform synchronization in the limbic system in vitro. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;68:167–207. - PubMed
-
- Bang H, Kim Y, Kim D. TREK-2, a new member of the mechanosensitive tandem-pore K+ channel family. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:17412–17419. - PubMed
-
- Bayliss DA, Sirois JE, Talley EM. The TASK family: two-pore domain background K+ channels. Mol Interv. 2003;3:205–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

