UNC-83 is a nuclear-specific cargo adaptor for kinesin-1-mediated nuclear migration
- PMID: 19605495
- PMCID: PMC2730402
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.038596
UNC-83 is a nuclear-specific cargo adaptor for kinesin-1-mediated nuclear migration
Abstract
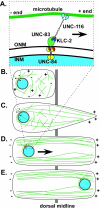
Intracellular nuclear migration is essential for many cellular events including fertilization, establishment of polarity, division and differentiation. How nuclei migrate is not understood at the molecular level. The C. elegans KASH protein UNC-83 is required for nuclear migration and localizes to the outer nuclear membrane. UNC-83 interacts with the inner nuclear membrane SUN protein UNC-84 and is proposed to connect the cytoskeleton to the nuclear lamina. Here, we show that UNC-83 also interacts with the kinesin-1 light chain KLC-2, as identified in a yeast two-hybrid screen and confirmed by in vitro assays. UNC-83 interacts with and recruits KLC-2 to the nuclear envelope in a heterologous tissue culture system. Additionally, analysis of mutant phenotypes demonstrated that both KLC-2 and the kinesin-1 heavy chain UNC-116 are required for nuclear migration. Finally, the requirement for UNC-83 in nuclear migration could be partially bypassed by expressing a synthetic outer nuclear membrane KLC-2::KASH fusion protein. Our data support a model in which UNC-83 plays a central role in nuclear migration by acting to bridge the nuclear envelope and as a kinesin-1 cargo-specific adaptor so that motor-generated forces specifically move the nucleus as a single unit.
Figures
Similar articles
-
UNC-83 IS a KASH protein required for nuclear migration and is recruited to the outer nuclear membrane by a physical interaction with the SUN protein UNC-84.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Apr;17(4):1790-801. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-09-0894. Epub 2006 Feb 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16481402 Free PMC article.
-
toca-1 is in a novel pathway that functions in parallel with a SUN-KASH nuclear envelope bridge to move nuclei in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2013 Jan;193(1):187-200. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.146589. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23150597 Free PMC article.
-
UNC-83 coordinates kinesin-1 and dynein activities at the nuclear envelope during nuclear migration.Dev Biol. 2010 Feb 15;338(2):237-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.12.004. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20005871 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between nuclei and the cytoskeleton are mediated by SUN-KASH nuclear-envelope bridges.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010;26:421-44. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100109-104037. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20507227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connecting the nucleus to the cytoskeleton by SUN-KASH bridges across the nuclear envelope.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;25(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.10.014. Epub 2012 Nov 10. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23149102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hubbing the Cancer Cell.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;14(23):5924. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235924. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The branched actin nucleator Arp2/3 promotes nuclear migrations and cell polarity in the C. elegans zygote.Dev Biol. 2011 Sep 15;357(2):356-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.07.008. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21798253 Free PMC article.
-
LINC complexes promote homologous recombination in part through inhibition of nonhomologous end joining.J Cell Biol. 2016 Dec 19;215(6):801-821. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201604112. Epub 2016 Dec 12. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27956467 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear migration events throughout development.J Cell Sci. 2016 May 15;129(10):1951-61. doi: 10.1242/jcs.179788. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 27182060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FLN-2 functions in parallel to LINC complexes and Cdc42/actin pathways during P-cell nuclear migration through constricted spaces in Caenorhabditis elegans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 6:2023.08.04.552041. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.04.552041. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Genetics. 2024 Jul 8;227(3):iyae071. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae071. PMID: 37577634 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bowman, A. B., Kamal, A., Ritchings, B. W., Philp, A. V., McGrail, M., Gindhart, J. G. and Goldstein, L. S. (2000). Kinesin-dependent axonal transport is mediated by the sunday driver (SYD) protein. Cell 103, 583-594. - PubMed
-
- Fan, J. and Beck, K. A. (2004). A role for the spectrin superfamily member Syne-1 and kinesin II in cytokinesis. J. Cell Sci. 117, 619-629. - PubMed
-
- Gindhart, J. G. (2006). Towards an understanding of kinesin-1 dependent transport pathways through the study of protein-protein interactions. Brief. Funct. Genomic. Proteomic. 5, 74-86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

