AP-1 activated by toll-like receptors regulates expression of IL-23 p19
- PMID: 19592489
- PMCID: PMC2781995
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.025528
AP-1 activated by toll-like receptors regulates expression of IL-23 p19
Abstract
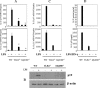
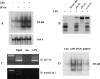
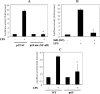
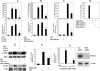
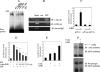
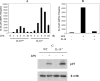
Interleukin (IL)-23, a new member of the IL-12 family, plays a central role in the Th17 immune response and in autoimmune diseases. It is clear that activated macrophages and dendritic cells produce IL-23, but the molecular mechanisms whereby inflammatory signals stimulate IL-23 expression are not fully understood. We demonstrate that induction of IL-23 p19 gene expression by LPS depends on the TLR4 and MyD88 pathways. All three MAPK pathways (ERK, JNK, and p38) that are activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation were shown to exert a positive effect on p19 expression. We cloned a 1.3-kb putative p19 promoter and defined its transcription initiation sites by the 5'-rapid amplification of cDNA ends method. By analyzing IL-23 p19 promoter mutants, we have identified a promoter region (-413 to +10) that contains several important elements, including NF-kappaB and AP-1. In addition to NF-kappaB, we have demonstrated that the proximal AP-1 site is important for p19 promoter activation. Mutation of the AP-1 site resulted in the loss of p19 promoter activation. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) analysis showed that c-Jun and c-Fos bind to the AP-1 site, which was confirmed by a chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. Furthermore, co-transfection of c-Jun and ATF2 synergistically induced p19 promoter activation, and c-Jun and ATF2 formed a protein complex, demonstrated by co-immunoprecipitation. Finally, LPS-stimulated peritoneal macrophages from IL-10-deficient mice expressed significantly higher IL-23 p19 than macrophages from wild type mice, and the addition of recombinant IL-10 strongly inhibited LPS-induced p19 expression. Thus, this study suggests that MyD88-dependent Toll-like receptor signaling induces IL-23 p19 gene expression through both MAPKs and NF-kappaB.
Figures

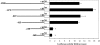
Similar articles
-
IL-17R activation of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts induces IL-23 p19 production: Differential involvement of NF-κB versus JNK/AP-1 pathways.Mol Immunol. 2011 Jan;48(4):647-56. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.11.008. Epub 2010 Dec 8. Mol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21145111
-
A proximal kappaB site in the IL-23 p19 promoter is responsible for RelA- and c-Rel-dependent transcription.J Immunol. 2007 Nov 15;179(10):6596-603. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.6596. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17982049
-
Promoter analysis reveals critical roles for SMAD-3 and ATF-2 in expression of IL-23 p19 in macrophages.J Immunol. 2008 Oct 1;181(7):4523-33. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.7.4523. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18802055
-
Emerging roles of ATF2 and the dynamic AP1 network in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Jan;10(1):65-76. doi: 10.1038/nrc2681. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20029425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of phages in autoimmune liver diseases.Clin Exp Immunol. 2018 Apr;192(1):1-6. doi: 10.1111/cei.13092. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29266228 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How sphingolipids affect T cells in the resolution of inflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 13;13:1002915. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1002915. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36176439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of interleukin-23 p19 by serum amyloid A (SAA) in rheumatoid synoviocytes.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Nov;162(2):244-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04242.x. Epub 2010 Sep 14. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20840651 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 23 and autoimmune diseases: current and possible future therapies.Inflamm Res. 2020 May;69(5):463-480. doi: 10.1007/s00011-020-01339-9. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Inflamm Res. 2020. PMID: 32215665 Review.
-
The unfolded protein response and the phosphorylations of activating transcription factor 2 in the trans-activation of il23a promoter produced by β-glucans.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 15;289(33):22942-22957. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.522656. Epub 2014 Jun 30. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24982422 Free PMC article.
-
ANKRD22 promotes resolution of psoriasiform skin inflammation by antagonizing NIK-mediated IL-23 production.Mol Ther. 2024 May 1;32(5):1561-1577. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.03.007. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38454607
References
-
- Oppmann B., Lesley R., Blom B., Timans J. C., Xu Y., Hunte B., Vega F., Yu N., Wang J., Singh K., Zonin F., Vaisberg E., Churakova T., Liu M., Gorman D., Wagner J., Zurawski S., Liu Y., Abrams J. S., Moore K. W., Rennick D., de Waal-Malefyt R., Hannum C., Bazan J. F., Kastelein R. A. (2000) Immunity 13, 715–725 - PubMed
-
- Hunter C. A. (2005) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5, 521–531 - PubMed
-
- Kastelein R. A., Hunter C. A., Cua D. J. (2007) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25, 221–242 - PubMed
-
- McKenzie B. S., Kastelein R. A., Cua D. J. (2006) Trends Immunol. 27, 17–23 - PubMed
-
- Langrish C. L., McKenzie B. S., Wilson N. J., de Waal Malefyt R., Kastelein R. A., Cua D. J. (2004) Immunol. Rev. 202, 96–105 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

