MicroRNA miR-29 modulates expression of immunoinhibitory molecule B7-H3: potential implications for immune based therapy of human solid tumors
- PMID: 19584290
- PMCID: PMC2719680
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4517
MicroRNA miR-29 modulates expression of immunoinhibitory molecule B7-H3: potential implications for immune based therapy of human solid tumors
Abstract
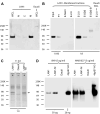
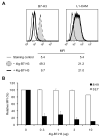
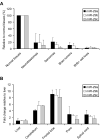
B7-H3, a surface immunomodulatory glycoprotein, inhibits natural killer cells and T cells. The monoclonal antibody (mAb) 8H9 is specific for 4Ig-B7-H3, the long and principal form of B7-H3. Early results from radioimmunotherapy using 8H9 have shown promise in patients with metastatic solid tumors to the central nervous system. Whereas B7-H3 transcript was ubiquitously expressed in a wide spectrum of human solid tumors as well as human normal tissues, B7-H3 protein was preferentially expressed only in tumor tissues. By quantitative reverse transcription-PCR, all three isoforms of microRNA miR-29 (a, b, and c) were highly expressed in normal tissues. However, they were down-regulated in a broad spectrum of solid tumors, including neuroblastoma, sarcomas, brain tumors, and tumor cell lines. B7-H3 protein expression was inversely correlated with miR-29 levels in both cell lines and tumor tissues tested. Using luciferase reporter assay, miR-29a was shown to directly target B7-H3 3' untranslated region, and knock-in and knockdown of miR-29a led to down-regulation and up-regulation, respectively, of B7-H3 protein expression. The ability of miR-29 to control B7-H3 protein expression has implications in immune escape by solid tumors. Differential modulation of this key immunoinhibitory molecule in tumor versus normal tissues may advance both cell-mediated immunotherapy and antibody-based targeted strategies using the B7-H3-specific mAb 8H9.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

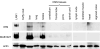
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA miR-29a Inhibits Colon Cancer Progression by Downregulating B7-H3 Expression: Potential Molecular Targets for Colon Cancer Therapy.Mol Biotechnol. 2021 Sep;63(9):849-861. doi: 10.1007/s12033-021-00348-1. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Mol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34100183
-
Expression and regulation of B7-H3 immunoregulatory receptor, in human mesothelial and mesothelioma cells: immunotherapeutic implications.J Cell Physiol. 2011 Oct;226(10):2595-600. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22600. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21792917
-
Clinical importance of B7-H3 expression in human pancreatic cancer.Br J Cancer. 2009 Nov 17;101(10):1709-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605375. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Br J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19844235 Free PMC article.
-
B7-H3 in tumors: friend or foe for tumor immunity?Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018 Feb;81(2):245-253. doi: 10.1007/s00280-017-3508-1. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29299639 Review.
-
B7-H3-targeted CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumors.Int Rev Immunol. 2022;41(6):625-637. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2022.2102619. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Int Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35855615 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential role of miRNAs in orchestrating the biology of the tumor microenvironment.Mol Cancer. 2016 May 26;15(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0525-3. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27231010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA miR-29a Inhibits Colon Cancer Progression by Downregulating B7-H3 Expression: Potential Molecular Targets for Colon Cancer Therapy.Mol Biotechnol. 2021 Sep;63(9):849-861. doi: 10.1007/s12033-021-00348-1. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Mol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34100183
-
B7-H3, a potential therapeutic target, is expressed in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma.J Neurooncol. 2013 Feb;111(3):257-64. doi: 10.1007/s11060-012-1021-2. Epub 2012 Dec 12. J Neurooncol. 2013. PMID: 23232807 Free PMC article.
-
UV-type specific alteration of miRNA expression and its association with tumor progression and metastasis in SCC cell lines.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Dec;146(12):3215-3231. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03358-9. Epub 2020 Aug 31. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32865618
-
Immunotherapy targets in pediatric cancer.Front Oncol. 2012 Jan 30;2:3. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00003. eCollection 2012. Front Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22645714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flies DB, Chen L. The new B7s: playing a pivotal role in tumor immunity. J Immunother. 2007;30:251–60. - PubMed
-
- Chapoval AI, Ni J, Lau JS, et al. B7-H3: a costimulatory molecule for T cell activation and IFN-gamma production. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:269–74. - PubMed
-
- Steinberger P, Majdic O, Derdak SV, et al. Molecular characterization of human 4Ig-B7-H3, a member of the B7 family with four Ig-like domains. J Immunol. 2004;172:2352–9. - PubMed
-
- Sun M, Richards S, Prasad DV, Mai XM, Rudensky A, Dong C. Characterization of mouse and human B7-H3 genes. J Immunol. 2002;168:6294–7. - PubMed
-
- Suh WK, Gajewska BU, Okada H, et al. The B7 family member B7-H3 preferentially down-regulates T helper type 1-mediated immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:899–906. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

