Epigenetic reprogramming during wound healing: loss of polycomb-mediated silencing may enable upregulation of repair genes
- PMID: 19575012
- PMCID: PMC2726669
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2009.102
Epigenetic reprogramming during wound healing: loss of polycomb-mediated silencing may enable upregulation of repair genes
Abstract
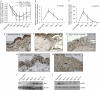
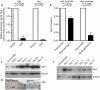
Tissue repair is a complex process that requires wound-edge cells to proliferate and migrate, which in turn necessitates induction of a large repair transcriptome. Epigenetic modifications have emerged as crucial regulators of gene expression. Here, we ask whether epigenetic reprogramming might contribute to the concerted induction of repair genes by wound-edge cells. Polycomb group proteins (PcGs) co-operatively silence genes by laying down repressive marks such as histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3), which can be removed by specific demethylases. We show that PcGs Eed, Ezh2 and Suz12 are significantly downregulated during murine skin repair, whereas the newly described demethylases Jmjd3 and Utx are markedly upregulated. Correspondingly, we find a striking reduction of repressive H3K27me3 in the wound epidermis. Quantitative chromatin immunoprecipitation studies have revealed that there is less Eed bound to the regulatory regions of two paradigm wound-induced genes, Myc and Egfr, suggesting that loss of polycomb-mediated silencing might contribute to the induction of repair genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of JmjC domain-containing UTX and JMJD3 as histone H3 lysine 27 demethylases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Nov 20;104(47):18439-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707292104. Epub 2007 Nov 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18003914 Free PMC article.
-
An EZ mark to miss.Cell Stem Cell. 2008 Dec 4;3(6):577-8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.11.007. Cell Stem Cell. 2008. PMID: 19041770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors deplete enhancer of zeste 2 and associated polycomb repressive complex 2 proteins in human acute leukemia cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Dec;5(12):3096-104. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0418. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. PMID: 17172412
-
Down-regulation of the histone methyltransferase EZH2 contributes to the epigenetic programming of decidualizing human endometrial stromal cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Nov;25(11):1892-903. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1139. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21903722 Free PMC article.
-
JMJD3 as an epigenetic regulator in development and disease.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;67:148-57. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26193001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ATF4-dependent regulation of the JMJD3 gene during amino acid deprivation can be rescued in Atf4-deficient cells by inhibition of deacetylation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 19;287(43):36393-403. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.399600. Epub 2012 Sep 6. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22955275 Free PMC article.
-
The fidelity of dynamic signaling by noisy biomolecular networks.PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(3):e1002965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002965. Epub 2013 Mar 28. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 23555208 Free PMC article.
-
The histone demethylase UTX enables RB-dependent cell fate control.Genes Dev. 2010 Feb 15;24(4):327-32. doi: 10.1101/gad.1882610. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20123895 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of Jumonji-type oxygenases in human disease.Epigenomics. 2014 Feb;6(1):89-120. doi: 10.2217/epi.13.79. Epigenomics. 2014. PMID: 24579949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidermal stem cells and their epigenetic regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Aug 30;14(9):17861-80. doi: 10.3390/ijms140917861. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23999591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agger K, Cloos PA, Christensen J, Pasini D, Rose S, Rappsilber J, Issaeva I, Canaani E, Salcini AE, Helin K (2007) UTX and JMJD3 are histone H3K27 demethylases involved in HOX gene regulation and development. Nature 449: 731–734 - PubMed
-
- Boyer LA et al. (2006) Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature 441: 349–353 - PubMed
-
- Cao R, Wang L, Wang H, Xia L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Jones RS, Zhang Y (2002) Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science 298: 1039–1043 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

