The SESA network links duplication of the yeast centrosome with the protein translation machinery
- PMID: 19571182
- PMCID: PMC2704472
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.524209
The SESA network links duplication of the yeast centrosome with the protein translation machinery
Abstract
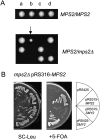
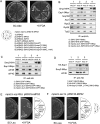
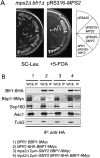
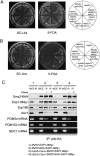
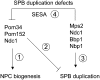
The yeast spindle pole body (SPB), the functional equivalent of mammalian centrosome, duplicates in G1/S phase of the cell cycle and then becomes inserted into the nuclear envelope. Here we describe a link between SPB duplication and targeted translation control. When insertion of the newly formed SPB into the nuclear envelope fails, the SESA network comprising the GYF domain protein Smy2, the translation inhibitor Eap1, the mRNA-binding protein Scp160 and the Asc1 protein, specifically inhibits initiation of translation of POM34 mRNA that encodes an integral membrane protein of the nuclear pore complex, while having no impact on other mRNAs. In response to SESA, POM34 mRNA accumulates in the cytoplasm and is not targeted to the ER for cotranslational translocation of the protein. Reduced level of Pom34 is sufficient to restore viability of mutants with defects in SPB duplication. We suggest that the SESA network provides a mechanism by which cells can regulate the translation of specific mRNAs. This regulation is used to coordinate competing events in the nuclear envelope.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pom34 protein level by SESA network is related to membrane lipid composition.FEMS Yeast Res. 2015 Dec;15(8):fov089. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/fov089. Epub 2015 Sep 28. FEMS Yeast Res. 2015. PMID: 26419396
-
Dhh1 is a member of the SESA network.Yeast. 2019 Feb;36(2):99-105. doi: 10.1002/yea.3363. Epub 2018 Nov 11. Yeast. 2019. PMID: 30346046
-
Yeast Eap1p, an eIF4E-associated protein, has a separate function involving genetic stability.Curr Biol. 2000 Nov 30;10(23):1519-22. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00829-0. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 11114520
-
Big Lessons from Little Yeast: Budding and Fission Yeast Centrosome Structure, Duplication, and Function.Annu Rev Genet. 2017 Nov 27;51:361-383. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120116-024733. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Annu Rev Genet. 2017. PMID: 28934593 Review.
-
Duplication of the Yeast Spindle Pole Body Once per Cell Cycle.Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Apr 15;36(9):1324-31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00048-16. Print 2016 May. Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26951196 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism and Regulation of Protein Synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2016 May;203(1):65-107. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.186221. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27183566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae spindle pole body remodeling factors.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 12;5(11):e15426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015426. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21103054 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila mRNA Localization During Later Development: Past, Present, and Future.Front Genet. 2019 Mar 7;10:135. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00135. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 30899273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sec66-Dependent Regulation of Yeast Spindle-Pole Body Duplication Through Pom152.Genetics. 2015 Dec;201(4):1479-95. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.178012. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 26510791 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of RNA-Binding Protein Targets with HyperTRIBE in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 20;24(10):9033. doi: 10.3390/ijms24109033. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alber F, Dokudovskaya S, Veenhoff LM, Zhang W, Kipper J, Devos D, Suprapto A, Karni-Schmidt O, Williams R, Chait BT, et al. Determining the architectures of macromolecular assemblies. Nature. 2007a;450:683–694. - PubMed
-
- Alber F, Dokudovskaya S, Veenhoff LM, Zhang W, Kipper J, Devos D, Suprapto A, Karni-Schmidt O, Williams R, Chait BT, et al. The molecular architecture of the nuclear pore complex. Nature. 2007b;450:695–701. - PubMed
-
- Araki Y, Lau CK, Maekawa H, Jaspersen SL, Giddings JTH, Schiebel E, Winey M. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae spindle pole body (SPB) component Nbp1p is required for SPB membrane insertion and interacts with the integral membrane proteins Ndc1p and Mps2p. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:1959–1970. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
