Genomic antagonism between retinoic acid and estrogen signaling in breast cancer
- PMID: 19563758
- PMCID: PMC3374131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.043
Genomic antagonism between retinoic acid and estrogen signaling in breast cancer
Abstract
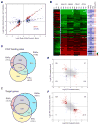
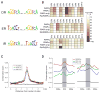
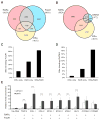
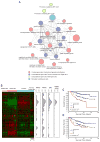
Retinoic acid (RA) triggers antiproliferative effects in tumor cells, and therefore RA and its synthetic analogs have great potential as anticarcinogenic agents. Retinoic acid receptors (RARs) mediate RA effects by directly regulating gene expression. To define the genetic network regulated by RARs in breast cancer, we identified RAR genomic targets using chromatin immunoprecipitation and expression analysis. We found that RAR binding throughout the genome is highly coincident with estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) binding, resulting in a widespread crosstalk of RA and estrogen signaling to antagonistically regulate breast cancer-associated genes. ERalpha- and RAR-binding sites appear to be coevolved on a large scale throughout the human genome, often resulting in competitive binding activity at nearby or overlapping cis-regulatory elements. The highly coordinated intersection between these two critical nuclear hormone receptor signaling pathways provides a global mechanism for balancing gene expression output via local regulatory interactions dispersed throughout the genome.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of trans-retinoic acid-resistant human breast cancer cell growth by retinoid X receptor-selective retinoids.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Nov;17(11):6598-608. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.11.6598. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9343423 Free PMC article.
-
Cross talk between progesterone receptors and retinoic acid receptors in regulation of cytokeratin 5-positive breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2017 Nov 2;36(44):6074-6084. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.204. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28692043 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoid-resistant estrogen receptor-negative human breast carcinoma cells transfected with retinoic acid receptor-alpha acquire sensitivity to growth inhibition by retinoids.J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 26;269(34):21440-7. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 8063776
-
Retinoid receptors in human lung cancer and breast cancer.Mutat Res. 1996 Feb 19;350(1):267-77. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(95)00102-6. Mutat Res. 1996. PMID: 8657191 Review.
-
Insufficient support for retinoic acid receptor control of synaptic plasticity through a non-genomic mechanism.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2023 Oct;71:101099. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2023.101099. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37647946 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ALDH1A1 drives prostate cancer metastases and radioresistance by interplay with AR- and RAR-dependent transcription.Theranostics. 2024 Jan 1;14(2):714-737. doi: 10.7150/thno.88057. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38169509 Free PMC article.
-
SMARCD1 is a "Goldilocks" metastasis modifier.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 29:2024.01.24.577061. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.24.577061. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 10;7(1):1299. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07018-3. PMID: 38410477 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Pan-cancer analyses of the nuclear receptor superfamily.Nucl Receptor Res. 2015 Dec;2:101182. doi: 10.11131/2015/101182. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Nucl Receptor Res. 2015. PMID: 27200367 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoid X receptor gamma (RXRG) is an independent prognostic biomarker in ER-positive invasive breast cancer.Br J Cancer. 2019 Oct;121(9):776-785. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0589-0. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Br J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31558802 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide binding patterns of thyroid hormone receptor beta.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 18;9(2):e81186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081186. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24558356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altucci L, Leibowitz MD, Ogilvie KM, de Lera AR, Gronemeyer H. RAR and RXR modulation in cancer and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:793–810. - PubMed
-
- Ansel KM, Djuretic I, Tanasa B, Rao A. Regulation of Th2 differentiation and Il4 locus accessibility. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:607–656. - PubMed
-
- Balmer JE, Blomhoff R. Gene expression regulation by retinoic acid. J Lipid Res. 2002;43:1773–1808. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Kamal M, Lindblad-Toh K, Bekiranov S, Bailey DK, Huebert DJ, McMahon S, Karlsson EK, Kulbokas EJ, 3rd, Gingeras TR, et al. Genomic maps and comparative analysis of histone modifications in human and mouse. Cell. 2005;120:169–181. - PubMed
-
- Carroll JS, Liu XS, Brodsky AS, Li W, Meyer CA, Szary AJ, Eeckhoute J, Shao W, Hestermann EV, Geistlinger TR, et al. Chromosome-wide mapping of estrogen receptor binding reveals long-range regulation requiring the forkhead protein FoxA1. Cell. 2005;122:33–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

