Resveratrol blocks interleukin-18-EMMPRIN cross-regulation and smooth muscle cell migration
- PMID: 19561311
- PMCID: PMC2724205
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00311.2009
Resveratrol blocks interleukin-18-EMMPRIN cross-regulation and smooth muscle cell migration
Abstract
Vascular smooth muscle cell (SMC) migration is an important mechanism in atherogenesis and postangioplasty arterial remodeling. Previously, we demonstrated that the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-18 is a potent inducer of SMC migration. Since extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) stimulates ECM degradation and facilitates cell migration, we investigated whether IL-18 and EMMPRIN regulate each other's expression, whether their cross talk induces SMC migration, and whether the phytoalexin resveratrol inhibits IL-18-EMMPRIN signaling and SMC migration. Our studies demonstrate that 1) IL-18 induces EMMPRIN mRNA and protein expressions and stimulates EMMPRIN secretion from human aortic SMCs; 2) IL-18 stimulates EMMPRIN expression via oxidative stress and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt-ERK signaling; 3) IL-18-stimulated SMC migration is significantly blunted by EMMPRIN knockdown, EMMPRIN function-blocking antibodies, or adenoviral transduction of mutant EMMPRIN; 4) conversely, EMMPRIN stimulates IL-18 expression and secretion via PI3K, Akt, and ERK; and 5) resveratrol attenuates IL-18- and EMMPRIN-mediated PI3K, Akt, and ERK activations; blunts IL-18-mediated oxidative stress; blocks IL-18-EMMPRIN cross-regulation; and inhibits SMC migration. Collectively, our results demonstrate that the coexpression and regulation of IL-18 and EMMPRIN in the vessel wall may amplify the inflammatory cascade and promote atherosclerosis and remodeling. Resveratrol, via its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, has the potential to inhibit the progression of atherosclerosis by blocking IL-18 and EMMPRIN cross-regulation and SMC migration.
Figures
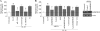
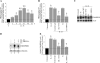
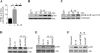
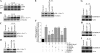

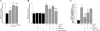
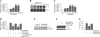
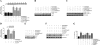
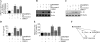
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-18-induced human coronary artery smooth muscle cell migration is dependent on NF-kappaB- and AP-1-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and is inhibited by atorvastatin.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jun 2;281(22):15099-109. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600200200. Epub 2006 Mar 22. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16554298
-
EMMPRIN activates multiple transcription factors in cardiomyocytes, and induces interleukin-18 expression via Rac1-dependent PI3K/Akt/IKK/NF-kappaB andMKK7/JNK/AP-1 signaling.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Oct;49(4):655-63. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.05.007. Epub 2010 Jun 9. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20538003 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol inhibits high glucose-induced PI3K/Akt/ERK-dependent interleukin-17 expression in primary mouse cardiac fibroblasts.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 May;294(5):H2078-87. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01363.2007. Epub 2008 Feb 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18310510
-
Contribution of vascular cell-derived cytokines to innate and inflammatory pathways in atherogenesis.J Cell Mol Med. 2011 Mar;15(3):484-500. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01245.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21199323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol inhibiting TGF/ERK signaling pathway can improve atherosclerosis: backgrounds, mechanisms and effects.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Nov;155:113775. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113775. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36271557 Review.
Cited by
-
Resveratrol, wine, and atherosclerosis.Int J Angiol. 2012 Mar;21(1):7-18. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1306417. Int J Angiol. 2012. PMID: 23450206 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol Abrogates Hypoxia-Induced Up-Regulation of Exosomal Amyloid-β Partially by Inhibiting CD147.Neurochem Res. 2019 May;44(5):1113-1126. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02742-3. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 30771155
-
Resveratrol in cardiovascular disease: what is known from current research?Heart Fail Rev. 2012 May;17(3):437-48. doi: 10.1007/s10741-011-9260-4. Heart Fail Rev. 2012. PMID: 21688187 Review.
-
Inhibitory effects of resveratrol on PDGF-BB-induced retinal pigment epithelial cell migration via PDGFRβ, PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56819. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056819. Epub 2013 Feb 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23457620 Free PMC article.
-
WNT1-inducible signaling pathway protein-1 activates diverse cell survival pathways and blocks doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte death.Cell Signal. 2010 May;22(5):809-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.01.005. Epub 2010 Jan 13. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20074638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araim O, Ballantyne J, Waterhouse AL, Sumpio BE. Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation with red wine and red wine polyphenols. J Vasc Surg 35: 1226–1232, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Baumer AT, Ten Freyhaus H, Sauer H, Wartenberg M, Kappert K, Schnabel P, Konkol C, Hescheler J, Vantler M, Rosenkranz S. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent membrane recruitment of Rac-1 and p47phox is critical for alpha-platelet-derived growth factor receptor-induced production of reactive oxygen species. J Biol Chem 283: 7864–7876, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Belguendouz L, Fremont L, Linard A. Resveratrol inhibits metal ion-dependent and independent peroxidation of porcine low-density lipoproteins. Biochem Pharmacol 53: 1347–1355, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Biswas C, Zhang Y, DeCastro R, Guo H, Nakamura T, Kataoka H, Nabeshima K. The human tumor cell-derived collagenase stimulatory factor (renamed EMMPRIN) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cancer Res 55: 434–439, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Cain RJ, Ridley AJ. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases in cell migration. Biol Cell 101: 13–29, 2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

