A combinatorial mechanism for determining the specificity of E2F activation and repression
- PMID: 19543322
- PMCID: PMC2726897
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.153
A combinatorial mechanism for determining the specificity of E2F activation and repression
Abstract
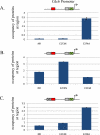
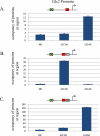
Various studies have detailed the role of E2F proteins in both transcription activation and repression. Further study has shown that distinct promoter elements, but comprising the same E2F-recognition motif, confer positive or negative E2F control and that this reflects binding of either activator or repressor E2F proteins, respectively. We now show that the specificity of binding of an activator or repressor E2F protein is determined by adjacent sequences that bind a cooperating transcription factor. We propose that the functional E2F element is a module comprising not only the E2F-binding site but also the adjacent site for the cooperating transcription factor.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Distinct recruitment of E2F family members to specific E2F-binding sites mediates activation and repression of the E2F1 promoter.Oncogene. 2003 Oct 23;22(48):7632-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206840. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 14576826
-
E2Fs link the control of G1/S and G2/M transcription.EMBO J. 2004 Nov 24;23(23):4615-26. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600459. Epub 2004 Oct 28. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15510213 Free PMC article.
-
E2F sites in the Op18 promoter are required for high level of expression in the human prostate carcinoma cell line PC-3-M.Gene. 2004 Oct 27;341:209-18. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.06.052. Gene. 2004. PMID: 15474303
-
E2F1-mediated transcriptional inhibition of the plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 gene.Eur J Biochem. 2001 Sep;268(18):4969-78. doi: 10.1046/j.0014-2956.2001.02428.x. Eur J Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11559366
-
A B-myb promoter corepressor site facilitates in vivo occupation of the adjacent E2F site by p107 x E2F and p130 x E2F complexes.J Biol Chem. 2002 Oct 11;277(41):39015-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202960200. Epub 2002 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12147683
Cited by
-
Low E2F2 activity is associated with high genomic instability and PARPi resistance.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 21;10(1):17948. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74877-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33087787 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for autoregulation and cell signaling pathway regulation from genome-wide binding of the Drosophila retinoblastoma protein.G3 (Bethesda). 2012 Nov;2(11):1459-72. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.004424. Epub 2012 Nov 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 23173097 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omic approach identifies a transcriptional network coupling innate immune response to proliferation in the blood of COVID-19 cancer patients.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 29;12(11):1019. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04299-y. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34716309 Free PMC article.
-
The Rb/E2F pathway modulates neurogenesis through direct regulation of the Dlx1/Dlx2 bigene cluster.J Neurosci. 2012 Jun 13;32(24):8219-30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1344-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22699903 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic ETS fusions deregulate E2F3 target genes in Ewing sarcoma and prostate cancer.Genome Res. 2013 Nov;23(11):1797-809. doi: 10.1101/gr.151340.112. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23940108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aparicio O, Geisberg JV, Sekinger EA, Yang A, Moqtaderi Z, Struhl K. Chromatin immunoprecipitation for determining the association of proteins with specific genomic sequences in vivo. Curr Protoc Mol Biol, Chapter 21: Unit 21.3. 2005 - PubMed
-
- Araki K, Nakajima Y, Eto K, Ikeda MA. Distinct recruitment of E2F family members to specific E2F-binding sites mediates activation and repression of the E2F1 promoter. Oncogene. 2003;22:7632–41. - PubMed
-
- Bates S, Phillips AC, Clark PA, Stott F, Peters G, Ludwig RL, et al. p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature. 1998;395:124–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

