Cholinergic neural signals to the spleen down-regulate leukocyte trafficking via CD11b
- PMID: 19542466
- PMCID: PMC2806576
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802684
Cholinergic neural signals to the spleen down-regulate leukocyte trafficking via CD11b
Abstract
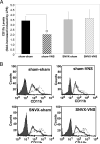
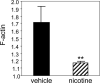
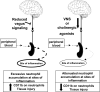
The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway is a physiological mechanism that inhibits cytokine production and diminishes tissue injury during inflammation. Recent studies demonstrate that cholinergic signaling reduces adhesion molecule expression and chemokine production by endothelial cells and suppresses leukocyte migration during inflammation. It is unclear how vagus nerve stimulation regulates leukocyte trafficking because the vagus nerve does not innervate endothelial cells. Using mouse models of leukocyte trafficking, we show that the spleen, which is a major point of control for cholinergic modulation of cytokine production, is essential for vagus nerve-mediated regulation of neutrophil activation and migration. Administration of nicotine, a pharmacologic agonist of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, significantly reduces levels of CD11b, a beta(2)-integrin involved in cell adhesion and leukocyte chemotaxis, on the surface of neutrophils in a dose-dependent manner and this function requires the spleen. Similarly, vagus nerve stimulation significantly attenuates neutrophil surface CD11b levels only in the presence of an intact and innervated spleen. Further mechanistic studies reveal that nicotine suppresses F-actin polymerization, the rate-limiting step for CD11b surface expression. These studies demonstrate that modulation of leukocyte trafficking via cholinergic signaling to the spleen is a specific, centralized neural pathway positioned to suppress the excessive accumulation of neutrophils at inflammatory sites. Activating this mechanism may have important therapeutic potential for preventing tissue injury during inflammation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cholinergic stimulation blocks endothelial cell activation and leukocyte recruitment during inflammation.J Exp Med. 2005 Apr 4;201(7):1113-23. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040463. J Exp Med. 2005. PMID: 15809354 Free PMC article.
-
Siglec-E is a negative regulator of acute pulmonary neutrophil inflammation and suppresses CD11b β2-integrin-dependent signaling.Blood. 2013 Mar 14;121(11):2084-94. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-08-449983. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23315163 Free PMC article.
-
Splenic nerve is required for cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway control of TNF in endotoxemia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Aug 5;105(31):11008-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803237105. Epub 2008 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18669662 Free PMC article.
-
β2 Integrin Signaling Cascade in Neutrophils: More Than a Single Function.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 18;11:619925. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.619925. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuro-immune interactions via the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.Life Sci. 2007 May 30;80(24-25):2325-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.01.002. Epub 2007 Jan 13. Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17289087 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk of nervous and immune systems in pancreatic cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Nov 30;11:1309738. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1309738. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38099290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve ameliorates inflammation and disease activity in a rat EAE model of multiple sclerosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 9;121(28):e2322577121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2322577121. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38968104 Free PMC article.
-
In a secondary analysis from a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial Dexmedetomidine blocks cholinergic dysregulation in delirium pathogenesis in patients with major surgery.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 9;13(1):3971. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30756-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36894596 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation in the treatment of disorders of consciousness: mechanisms and applications.Front Neurosci. 2023 Oct 18;17:1286267. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1286267. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37920298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streptococcus pyogenes M1T1 Variants Induce an Inflammatory Neutrophil Phenotype Including Activation of Inflammatory Caspases.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Jan 28;10:596023. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.596023. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33585270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pober JS, Sessa WC. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007;7:803–815. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC. The role of the endothelium in severe sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Blood. 2003;101:3765–3777. - PubMed
-
- Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI, Nourshargh S. Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007;7:678–689. - PubMed
-
- Muller WA. Leukocyte-endothelial-cell interactions in leukocyte transmigration and the inflammatory response. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:327–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

