Purification and functional reconstitution of monomeric mu-opioid receptors: allosteric modulation of agonist binding by Gi2
- PMID: 19542234
- PMCID: PMC2785361
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.026922
Purification and functional reconstitution of monomeric mu-opioid receptors: allosteric modulation of agonist binding by Gi2
Abstract
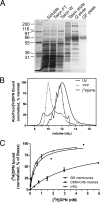
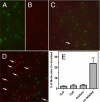
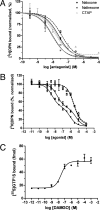
Despite extensive characterization of the mu-opioid receptor (MOR), the biochemical properties of the isolated receptor remain unclear. In light of recent reports, we proposed that the monomeric form of MOR can activate G proteins and be subject to allosteric regulation. A mu-opioid receptor fused to yellow fluorescent protein (YMOR) was constructed and expressed in insect cells. YMOR binds ligands with high affinity, displays agonist-stimulated [(35)S]guanosine 5'-(gamma-thio)triphosphate binding to Galpha(i), and is allosterically regulated by coupled G(i) protein heterotrimer both in insect cell membranes and as purified protein reconstituted into a phospholipid bilayer in the form of high density lipoprotein particles. Single-particle imaging of fluorescently labeled receptor indicates that the reconstituted YMOR is monomeric. Moreover, single-molecule imaging of a Cy3-labeled agonist, [Lys(7), Cys(8)]dermorphin, illustrates a novel method for studying G protein-coupled receptor-ligand binding and suggests that one molecule of agonist binds per monomeric YMOR. Together these data support the notion that oligomerization of the mu-opioid receptor is not required for agonist and antagonist binding and that the monomeric receptor is the minimal functional unit in regard to G protein activation and strong allosteric regulation of agonist binding by G proteins.
Figures
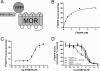
Similar articles
-
Biased μ-opioid receptor agonists diversely regulate lateral mobility and functional coupling of the receptor to its cognate G proteins.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;389(12):1289-1300. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1293-8. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27600870
-
The bovine mu-opioid receptor: cloning of cDNA and pharmacological characterization of the receptor expressed in mammalian cells.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999 Nov 10;73(1-2):129-37. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(99)00249-1. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10581406
-
Comparison of [Dmt1]DALDA and DAMGO in binding and G protein activation at mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003 Dec;307(3):947-54. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.054775. Epub 2003 Oct 8. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003. PMID: 14534366
-
Mu-delta opioid receptor functional interaction: Insight using receptor-G protein fusions.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Aug;318(2):683-90. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.101220. Epub 2006 May 11. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006. PMID: 16690720
-
[Effects of newly isolated opioid peptides on G-protein activation: usefulness of [35S] GTP gamma S binding study and its practical application].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1998 Aug;18(4):107-16. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1998. PMID: 9866825 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Dissecting non-coding RNA mechanisms in cellulo by Single-molecule High-Resolution Localization and Counting.Methods. 2013 Sep 15;63(2):188-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.05.028. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Methods. 2013. PMID: 23820309 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis of Opioid Action: From Structures to New Leads.Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Jan 1;87(1):6-14. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.08.028. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Biol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31653480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receptor-Receptor Interactions of G Protein-Coupled Receptors in the Carotid Body: A Working Hypothesis.Front Physiol. 2018 Jun 7;9:697. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00697. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29930516 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-Receptor Interactions as a Widespread Phenomenon: Novel Targets for Drug Development?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Feb 18;10:53. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00053. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30833931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic lateral organization of opioid receptors (kappa, muwt and muN40D ) in the plasma membrane at the nanoscale level.Traffic. 2018 May 28;19(9):690-709. doi: 10.1111/tra.12582. Online ahead of print. Traffic. 2018. PMID: 29808515 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

