LFA-1-dependent Ca2+ entry following suboptimal T cell receptor triggering proceeds without mobilization of intracellular Ca2+
- PMID: 19542227
- PMCID: PMC2755939
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.000752
LFA-1-dependent Ca2+ entry following suboptimal T cell receptor triggering proceeds without mobilization of intracellular Ca2+
Abstract
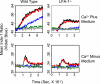
A surge in cytosolic calcium ion concentration by entry of extracellular Ca2+ is a hallmark of T cell activation. According to store-operated Ca2+ entry mechanism, the Ca2+ entry is preceded by activation of phospholipase C-gamma1 (PLC-gamma1) and the consequent mobilization of intracellular Ca2+. Using membrane vesicles expressing the mouse class I major histocompatibility complex, i.e. Ld plus costimulatory ligands, i.e. B7-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 along with 2C T cell receptor transgenic T cells, we investigated the roles of CD28 and LFA-1 (lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1) in the activation of PLC-gamma1 and Ca2+ signaling. Both CD28 and LFA-1 made significant and comparable contributions to the activation of PLC-gamma1 as gauged by the level of its phosphorylation at tyrosine 783. In contrast, their roles in Ca2+ signaling were quite distinct so that LFA-1/intercellular adhesion molecule-1 interaction exerted a determining role, whereas CD28/B7-1 interaction played only a minimal role. In particular, when the T cells were activated by suboptimal T cell receptor stimulation, LFA-1 played an indispensable role in the Ca2+ signaling. Further experiments using Ca2+-free medium demonstrated that the entry of extracellular Ca2+ was not always accompanied by mobilization of intracellular Ca2+. Thus, intracellular Ca2+ mobilization was hardly detected under the condition that LFA-1 played the indispensable role in the entry of extracellular Ca2+, while a distinct level of intracellular Ca2+ mobilization was readily detected under the condition that LFA-1 played only the supporting role. These results ensure the unique role of LFA-1 in T cell Ca2+ signaling and reveal that LFA-1-dependent Ca2+ entry proceeds via a mechanism separate from store-operated Ca2+ entry.
Figures


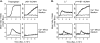

Similar articles
-
Beta 2-integrin LFA-1 signaling through phospholipase C-gamma 1 activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7099-103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7099. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 7688472 Free PMC article.
-
Role of intracellular Ca2+ levels in the regulation of CD11a/CD18 mediated cell adhesion.Cell Adhes Commun. 1993 May;1(1):21-32. doi: 10.3109/15419069309095679. Cell Adhes Commun. 1993. PMID: 7915956
-
Distinct roles for LFA-1 and CD28 during activation of naive T cells: adhesion versus costimulation.Immunity. 1997 Oct;7(4):549-57. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80376-3. Immunity. 1997. PMID: 9354475
-
T Cell Activation Pathways: B7, LFA-3, and ICAM-1 Shape Unique T Cell Profiles.Crit Rev Immunol. 2017;37(2-6):463-481. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.v37.i2-6.130. Crit Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29773030 Review.
-
T cell activation pathways: B7, LFA-3, and ICAM-1 shape unique T cell profiles.Crit Rev Immunol. 1995;15(3-4):235-53. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v15.i3-4.30. Crit Rev Immunol. 1995. PMID: 8834450 Review.
Cited by
-
Calpain 2 controls turnover of LFA-1 adhesions on migrating T lymphocytes.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 30;5(11):e15090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015090. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21152086 Free PMC article.
-
Acute inhibition of selected membrane-proximal mouse T cell receptor signaling by mitochondrial antagonists.PLoS One. 2009 Nov 10;4(11):e7738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007738. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19901985 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-mediated T cell absorption of antigen presenting cell-derived molecules.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jan 1;16(2):411-21. doi: 10.2741/3695. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011. PMID: 21196178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct patterns of cytolytic T-cell activation by different tumour cells revealed by Ca2+ signalling and granule mobilization.Immunology. 2017 Feb;150(2):199-212. doi: 10.1111/imm.12679. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 27716898 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiation of T Cell Stimulatory Activity by Chemical Fixation of a Weak Peptide-MHC Complex.Mol Cells. 2017 Jan;40(1):24-36. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2017.2218. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Mol Cells. 2017. PMID: 28152301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis R. S. (2001) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 497–521 - PubMed
-
- Quintana A., Griesemer D., Schwarz E. C., Hoth M. (2005) Pflugers Arch. 450, 1–12 - PubMed
-
- Feske S. (2007) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7, 690–702 - PubMed
-
- Evans R., Patzak I., Svensson L., De Filippo K., Jones K., McDowall A., Hogg N. (2009) J. Cell Sci. 122, 215–225 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

