The anterior insula in autism: under-connected and under-examined
- PMID: 19538989
- PMCID: PMC2743776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.06.002
The anterior insula in autism: under-connected and under-examined
Abstract
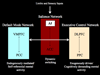
Autism is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder of unknown etiology. While the past decade has witnessed a proliferation of neuroimaging studies of autism, theoretical approaches for understanding systems-level brain abnormalities remain poorly developed. We propose a novel anterior insula-based systems-level model for investigating the neural basis of autism, synthesizing recent advances in brain network functional connectivity with converging evidence from neuroimaging studies in autism. The anterior insula is involved in interoceptive, affective and empathic processes, and emerging evidence suggests it is part of a "salience network" integrating external sensory stimuli with internal states. Network analysis indicates that the anterior insula is uniquely positioned as a hub mediating interactions between large-scale networks involved in externally and internally oriented cognitive processing. A recent meta-analysis identifies the anterior insula as a consistent locus of hypoactivity in autism. We suggest that dysfunctional anterior insula connectivity plays an important role in autism. Critical examination of these abnormalities from a systems neuroscience perspective should be a priority for further research on the neurobiology of autism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Altered functional organization within the insular cortex in adult males with high-functioning autism spectrum disorder: evidence from connectivity-based parcellation.Mol Autism. 2016 Oct 5;7:41. doi: 10.1186/s13229-016-0106-8. eCollection 2016. Mol Autism. 2016. PMID: 27713815 Free PMC article.
-
Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function.Brain Struct Funct. 2010 Jun;214(5-6):655-67. doi: 10.1007/s00429-010-0262-0. Epub 2010 May 29. Brain Struct Funct. 2010. PMID: 20512370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insula response and connectivity during social and non-social attention in children with autism.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016 Mar;11(3):433-44. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsv126. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26454817 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of structural covariance with functional connectivity approaches exemplified by an investigation of the left anterior insula.Neuroimage. 2014 Oct 1;99:269-80. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.05.030. Epub 2014 May 17. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24844743 Free PMC article.
-
Altered connectivity and action model formation in autism is autism.Neuroscientist. 2011 Aug;17(4):437-48. doi: 10.1177/1073858410392381. Epub 2011 Apr 5. Neuroscientist. 2011. PMID: 21467306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Concordance of white matter and gray matter abnormalities in autism spectrum disorders: a voxel-based meta-analysis study.Hum Brain Mapp. 2014 May;35(5):2073-98. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22313. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014. PMID: 23894001 Free PMC article.
-
Evoked and intrinsic brain network dynamics in children with autism spectrum disorder.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;28:102396. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102396. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32891039 Free PMC article.
-
Partially impaired functional connectivity states between right anterior insula and default mode network in autism spectrum disorder.Hum Brain Mapp. 2019 Mar;40(4):1264-1275. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24447. Epub 2018 Oct 27. Hum Brain Mapp. 2019. PMID: 30367744 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal immune activation alters social affective behavior and sensitivity to corticotropin releasing factor in male but not female rats.Horm Behav. 2023 Mar;149:105313. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2023.105313. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Horm Behav. 2023. PMID: 36706685 Free PMC article.
-
The Current View on the Paradox of Pain in Autism Spectrum Disorders.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Jul 22;13:910824. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.910824. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35935443 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adolphs R, Sears L, Piven J. Abnormal processing of social information from faces in autism. J Cogn Neurosci. 2001;13(2):232–240. - PubMed
-
- Allman J, Hakeem A, Watson K. Two phylogenetic specializations in the human brain. Neuroscientist. 2002;8(4):335–346. - PubMed
-
- Allman JM, Watson KK, Tetreault NA, Hakeem AY. Intuition and autism: a possible role for Von Economo neurons. Trends Cogn Sci. 2005;9(8):367–373. - PubMed
-
- Augustine JR. Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1996;22(3):229–244. - PubMed
-
- Baron-Cohen S, Ring HA, Bullmore ET, Wheelwright S, Ashwin C, Williams SC. The amygdala theory of autism. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2000;24(3):355–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

