Immediate breast tissue expander-implant reconstruction with inferolateral AlloDerm hammock and postoperative radiation: a preliminary report
- PMID: 19526050
- PMCID: PMC2683576
Immediate breast tissue expander-implant reconstruction with inferolateral AlloDerm hammock and postoperative radiation: a preliminary report
Abstract
Objective: To preserve the mastectomy skin envelope in select patients destined to receive radiation following mastectomy, we performed immediate tissue expander-implant reconstruction with a subpectoral tissue expander and an inferolateral AlloDerm hammock for complete implant coverage. We hypothesized that the AlloDerm hammock may allow greater intraoperative volume expansion and potentially avoid the need for an autologous construct.
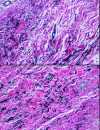
Methods: Tissue expanders were filled to 75%-85% capacity intraoperatively and 85%-100% prior to radiation therapy. This allowed for maximum preservation of the mastectomy skin envelope prior to radiation therapy and provided a sizable breast mound immediately following mastectomy. Histology of irradiated and nonirradiated capsules was compared.
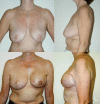
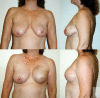
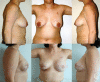
Results: Five patients aged 29-51 years had immediate implant (1) or expander-implant (4) breast reconstruction followed by postreconstruction radiation 2-6 months following the procedure. Patients were followed for 2.5-5.5 years following implant reconstruction and 2-5 years following radiation. No capsular contracture or implant loss was observed in any patient. No patients required or requested autologous reconstruction following radiation and all currently have silicone implants. Capsular biopsies from radiated and nonradiated implants showed identical collagen architecture on histology, confirming clinical observations.
Conclusion: Tissue expander-implant breast reconstruction following mastectomy preserves the skin envelope in patients who receive postmastectomy radiation. Further investigation is warranted to determine whether complete implant coverage with the pectoralis muscle and AlloDerm hammock mitigates the deleterious effects of radiation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inferolateral AlloDerm hammock for implant coverage in breast reconstruction.Ann Plast Surg. 2007 Sep;59(3):250-5. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e31802f8426. Ann Plast Surg. 2007. PMID: 17721209
-
Staged breast reconstruction with saline-filled implants in the irradiated breast: recent trends and therapeutic implications.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000 Mar;105(3):930-42. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200003000-00016. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000. PMID: 10724252
-
Breast reconstruction with implants, tissue expanders and AlloDerm: predicting volume and maximizing the skin envelope in skin sparing mastectomies.Breast J. 2010 Jan-Feb;16(1):14-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4741.2009.00866.x. Epub 2009 Nov 19. Breast J. 2010. PMID: 19929887
-
Radiation therapy and breast reconstruction: a critical review of the literature.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009 Aug;124(2):395-408. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181aee987. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009. PMID: 19644254 Review.
-
Radiation Modality (Proton/Photon), Timing, and Complication Rates in Patients With Breast Cancer Receiving 2-Stages Expander/Implant Reconstruction.Pract Radiat Oncol. 2022 Nov-Dec;12(6):475-486. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2022.05.017. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35989216 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Submuscular and Pre-Pectoral ADM Assisted Immediate Breast Reconstruction: A Literature Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 May 26;56(6):256. doi: 10.3390/medicina56060256. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32466619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TiLoop® Bra mesh used for immediate breast reconstruction: comparison of retropectoral and subcutaneous implant placement in a prospective single-institution series.Eur J Plast Surg. 2014;37(11):599-604. doi: 10.1007/s00238-014-1001-1. Epub 2014 Aug 3. Eur J Plast Surg. 2014. PMID: 25339795 Free PMC article.
-
Biological and synthetic mesh use in breast reconstructive surgery: a literature review.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Apr 21;14:121. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0874-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27102580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of the Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction Assessment Score on Expander-Based Reconstruction Success.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 28;13(21):6466. doi: 10.3390/jcm13216466. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39518605 Free PMC article.
-
Direct-to-implant breast reconstruction.Gland Surg. 2012 Nov;1(3):139-41. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2012.10.04. Gland Surg. 2012. PMID: 25083436 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgery. Plastic Surgery Procedural Statistics. 2008. Available at: www.plasticsurgery.org. - PubMed
-
- Breuing KH, Warren SM. Immediate bilateral breast reconstruction with implants and inferolateral AlloDerm slings. Ann Plast Surg. 2005;55:232–9. - PubMed
-
- Breuing KH, Colwell AS. Inferolateral AlloDerm hammock for implant coverage in breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2007;59:250–5. - PubMed
-
- Salzberg CA. Nonexpansive immediate breast reconstruction using human acellular tissue matrix graft (AlloDerm) Ann Plast Surg. 2006;57:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Zienowicz RJ, Karacaoglu E. Implant-based breast reconstruction with allograft. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;120:373–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
