JNK signalling modulates intestinal homeostasis and tumourigenesis in mice
- PMID: 19521338
- PMCID: PMC2711188
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.153
JNK signalling modulates intestinal homeostasis and tumourigenesis in mice
Abstract
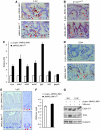
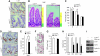
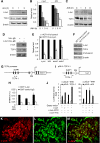
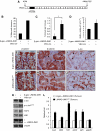
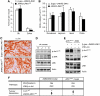
Wnt signalling is a crucial signalling pathway controlling intestinal homeostasis and cancer. We show here that the JNK MAP kinase pathway and one of its most important substrates, the AP-1 transcription factor c-Jun, modulates Wnt signalling strength in the intestine. Transgenic gut-specific augmentation of JNK signalling stimulated progenitor cell proliferation and migration, resulting in increased villus length. In the crypt, c-Jun protein was highly expressed in progenitor cells and the absence of c-Jun resulted in decreased proliferation and villus length. In addition to several known c-Jun/AP-1 target genes, expression of Wnt target genes Axin2 and Lgr5 were stimulated by JNK activation, suggesting a cross talk of JNK to Wnt signalling. Expression of the Wnt pathway component TCF4 was controlled by JNK activity, and chromatin immunoprecipitation and reporter assays identified tcf4 as a direct c-Jun target gene. Consequently, increased JNK activity accelerated tumourigenesis in a model of colorectal carcinogenesis. As c-jun is a direct target of the TCF4/beta-catenin complex, the control of tcf4 expression by JNK/c-Jun leads to a positive feedback loop that connects JNK and Wnt signalling. This mechanism regulates the physiological function of progenitor cells and oncogenic transformation.
Figures
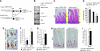
Similar articles
-
Interaction of phosphorylated c-Jun with TCF4 regulates intestinal cancer development.Nature. 2005 Sep 8;437(7056):281-5. doi: 10.1038/nature03914. Epub 2005 Jul 10. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16007074
-
Embryonic NANOG activity defines colorectal cancer stem cells and modulates through AP1- and TCF-dependent mechanisms.Stem Cells. 2012 Oct;30(10):2076-87. doi: 10.1002/stem.1182. Stem Cells. 2012. PMID: 22851508
-
Wnt-3a regulates chondrocyte differentiation via c-Jun/AP-1 pathway.FEBS Lett. 2005 Aug 29;579(21):4837-42. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.07.067. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 16099458
-
From JNK to pay dirt: jun kinases, their biochemistry, physiology and clinical importance.IUBMB Life. 2005 Apr-May;57(4-5):283-95. doi: 10.1080/15216540500097111. IUBMB Life. 2005. PMID: 16036612 Review.
-
The links between transcription, beta-catenin/JNK signaling, and carcinogenesis.Mol Cancer Res. 2009 Aug;7(8):1189-96. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0027. Epub 2009 Aug 11. Mol Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19671687 Review.
Cited by
-
The many faces and functions of β-catenin.EMBO J. 2012 Jun 13;31(12):2714-36. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.150. Epub 2012 May 22. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22617422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired Hippo signaling promotes Rho1-JNK-dependent growth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 27;112(4):1065-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415020112. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25583514 Free PMC article.
-
Bag1-L is a phosphorylation-dependent coactivator of c-Jun during neuronal apoptosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;30(15):3842-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01610-09. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20516211 Free PMC article.
-
RIP3 promotes colitis-associated colorectal cancer by controlling tumor cell proliferation and CXCL1-induced immune suppression.Theranostics. 2019 Jun 2;9(12):3659-3673. doi: 10.7150/thno.32126. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31281505 Free PMC article.
-
STRAP regulates c-Jun ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis and cellular proliferation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Apr 8;407(2):372-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.03.028. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21397588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angel P, Hattori K, Smeal T, Karin M (1988) The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP1. Cell 55: 875–885 - PubMed
-
- Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ, Clevers H (2007) Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature 449: 1003–1007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

