Inactivation of the C. elegans lipin homolog leads to ER disorganization and to defects in the breakdown and reassembly of the nuclear envelope
- PMID: 19494126
- PMCID: PMC2723152
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.044743
Inactivation of the C. elegans lipin homolog leads to ER disorganization and to defects in the breakdown and reassembly of the nuclear envelope
Abstract
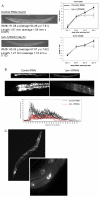
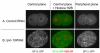
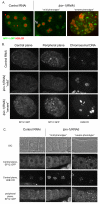
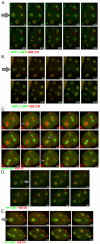
The nuclear envelope (NE) is a dynamic structure, undergoing periods of growth, breakdown and reassembly during the cell cycle. In yeast, altering lipid synthesis by inactivating the yeast homolog of lipin, a phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase, leads to disorganization of the peripheral ER and abnormal nuclear shape. These results suggest that lipid metabolism contributes to NE dynamics; however, since yeast undergo closed mitosis, the relevance of these observations to higher eukaryotes is unclear. In mammals, lipin has been implicated in adipose tissue differentiation, insulin resistance, lipid storage and obesity, but the underlying cellular defects caused by altering lipin levels are not known. Here, we identify the Caenorhabditis elegans lipin homolog (LPIN-1) and examine its affect on NE dynamics. We find that downregulating LPIN-1 by RNAi results in the appearance of membrane sheets and other abnormal structures in the peripheral ER. Moreover, lpin-1 RNAi causes defects in NE breakdown, abnormal chromosome segregation and irregular nuclear morphology. These results uncover cellular processes affected by lipin in metazoa, and suggest that lipid synthesis has a role in NE dynamics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipin is required for efficient breakdown of the nuclear envelope in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Cell Sci. 2009 Jun 15;122(Pt 12):1963-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.044750. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19494125
-
Spatial control of phospholipid flux restricts endoplasmic reticulum sheet formation to allow nuclear envelope breakdown.Genes Dev. 2014 Jan 15;28(2):121-6. doi: 10.1101/gad.230599.113. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24449268 Free PMC article.
-
Seipin is involved in the regulation of phosphatidic acid metabolism at a subdomain of the nuclear envelope in yeast.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Nov;1851(11):1450-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26275961
-
Coupling lipid synthesis with nuclear envelope remodeling.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Jan;47(1):52-65. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.08.009. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 34556392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What can Caenorhabditis elegans tell us about the nuclear envelope?FEBS Lett. 2007 Jun 19;581(15):2794-801. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.03.052. Epub 2007 Mar 30. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17418822 Review.
Cited by
-
The challenge of staying in shape: nuclear size matters.Curr Genet. 2021 Aug;67(4):605-612. doi: 10.1007/s00294-021-01176-1. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33779777 Review.
-
Phosphatidate phosphatase, a key regulator of lipid homeostasis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar;1831(3):514-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.08.006. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22910056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryo-fluorescence microscopy of high-pressure frozen C. elegans enables correlative FIB-SEM imaging of targeted embryonic stages in the intact worm.Methods Cell Biol. 2021;162:223-252. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2020.09.009. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Methods Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33707014 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed Encounter of Parental Genomes Can Lead to Aneuploidy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2018 Jan;208(1):139-151. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300289. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29150427 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans cyclin B3 is required for multiple mitotic processes including alleviation of a spindle checkpoint-dependent block in anaphase chromosome segregation.PLoS Genet. 2010 Nov 24;6(11):e1001218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001218. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 21124864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, D. J. and Hetzer, M. W. (2007). Nuclear envelope formation by chromatin-mediated reorganization of the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 1160-1166. - PubMed
-
- Ashrafi, K., Chang, F. Y., Watts, J. L., Fraser, A. G., Kamath, R. S., Ahringer, J. and Ruvkun, G. (2003). Genome-wide RNAi analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans fat regulatory genes. Nature 421, 268-272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

