Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy
- PMID: 19489737
- PMCID: PMC2835776
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.061906.092014
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy
Abstract
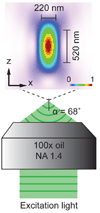
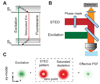
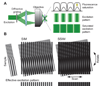
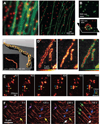
Achieving a spatial resolution that is not limited by the diffraction of light, recent developments of super-resolution fluorescence microscopy techniques allow the observation of many biological structures not resolvable in conventional fluorescence microscopy. New advances in these techniques now give them the ability to image three-dimensional (3D) structures, measure interactions by multicolor colocalization, and record dynamic processes in living cells at the nanometer scale. It is anticipated that super-resolution fluorescence microscopy will become a widely used tool for cell and tissue imaging to provide previously unobserved details of biological structures and processes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
3D super-resolution imaging by localization microscopy.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1232:123-36. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1752-5_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25331133
-
Visualizing and discovering cellular structures with super-resolution microscopy.Science. 2018 Aug 31;361(6405):880-887. doi: 10.1126/science.aau1044. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Science. 2018. PMID: 30166485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-speed super-resolution imaging of rotationally symmetric structures using SPEED microscopy and 2D-to-3D transformation.Nat Protoc. 2021 Jan;16(1):532-560. doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-00440-x. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Nat Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33318694 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in super-resolution fluorescence imaging and its applications in biology.J Genet Genomics. 2013 Dec 20;40(12):583-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Nov 23. J Genet Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24377865 Review.
-
Breaking the diffraction barrier: super-resolution imaging of cells.Cell. 2010 Dec 23;143(7):1047-58. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.002. Cell. 2010. PMID: 21168201 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Holotomography: Refractive Index as an Intrinsic Imaging Contrast for 3-D Label-Free Live Cell Imaging.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1310:211-238. doi: 10.1007/978-981-33-6064-8_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33834439
-
Subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence microscopy reveals a domain of the centrosome critical for pericentriolar material organization.Nat Cell Biol. 2012 Nov;14(11):1159-68. doi: 10.1038/ncb2597. Epub 2012 Oct 21. Nat Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23086239 Free PMC article.
-
Multiscale perspectives of virus entry via endocytosis.Virol J. 2013 Jun 5;10:177. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-177. Virol J. 2013. PMID: 23734580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantifying the minimum localization uncertainty of image scanning localization microscopy.Biophys Rep (N Y). 2024 Jan 20;4(1):100143. doi: 10.1016/j.bpr.2024.100143. eCollection 2024 Mar 13. Biophys Rep (N Y). 2024. PMID: 38380223 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasensitive and long-range transverse displacement metrology with polarization-encoded metasurface.Sci Adv. 2022 Oct 14;8(41):eadd1973. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.add1973. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36223465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hell SW, Wichmann J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated-emission: stimulated emission- depletion fluorescence microscopy. Opt. Lett. 1994;19:780–782. - PubMed
-
- Klar TA, Hell SW. Subdiffraction resolution in far-field fluorescence microscopy. Opt. Lett. 1999;24:954–956. - PubMed
-
- Hell SW. Far-field optical nanoscopy. Science. 2007;316:1153–1158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

