Cannabinoid receptor type 2 activation induces a microglial anti-inflammatory phenotype and reduces migration via MKP induction and ERK dephosphorylation
- PMID: 19476641
- PMCID: PMC2704199
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-25
Cannabinoid receptor type 2 activation induces a microglial anti-inflammatory phenotype and reduces migration via MKP induction and ERK dephosphorylation
Abstract
Background: Cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CBR2) inhibits microglial reactivity through a molecular mechanism yet to be elucidated. We hypothesized that CBR2 activation induces an anti-inflammatory phenotype in microglia by inhibiting extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway, via mitogen-activated protein kinase-phosphatase (MKP) induction. MKPs regulate mitogen activated protein kinases, but their role in the modulation of microglial phenotype is not fully understood.
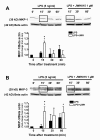
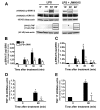
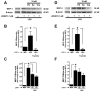
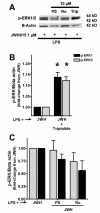
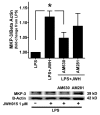
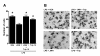
Results: JWH015 (a CBR2 agonist) increased MKP-1 and MKP-3 expression, which in turn reduced p-ERK1/2 in LPS-stimulated primary microglia. These effects resulted in a significant reduction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) expression and microglial migration. We confirmed the causative link of these findings by using MKP inhibitors. We found that the selective inhibition of MKP-1 by Ro-31-8220 and PSI2106, did not affect p-ERK expression in LPS+JWH015-treated microglia. However, the inhibition of both MKP-1 and MKP-3 by triptolide induced an increase in p-ERK expression and in microglial migration using LPS+JWH015-treated microglia.
Conclusion: Our results uncover a cellular microglial pathway triggered by CBR2 activation. These data suggest that the reduction of pro-inflammatory factors and microglial migration via MKP-3 induction is part of the mechanism of action of CBR2 agonists. These findings may have clinical implications for further drug development.
Figures
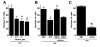
Similar articles
-
Spinal cannabinoid receptor type 2 agonist reduces mechanical allodynia and induces mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatases in a rat model of neuropathic pain.J Pain. 2012 Sep;13(9):836-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2012.05.013. Epub 2012 Aug 14. J Pain. 2012. PMID: 22901764 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase-3 (MKP-3) displays a p-JNK-MAPK substrate preference in astrocytes in vitro.Neurosci Lett. 2014 Jul 11;575:13-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.05.039. Epub 2014 May 23. Neurosci Lett. 2014. PMID: 24861519 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone suppresses monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 production via mitogen activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 dependent inhibition of Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in activated rat microglia.J Neurochem. 2007 Aug;102(3):667-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04535.x. Epub 2007 Apr 2. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17403137
-
Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatases (MKPs) in cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007 Dec;26(3-4):579-85. doi: 10.1007/s10555-007-9079-6. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007. PMID: 17717636 Review.
-
The role of MAP kinases and MAP kinase phosphatase-1 in resistance to breast cancer treatment.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010 Mar;29(1):143-9. doi: 10.1007/s10555-010-9208-5. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010. PMID: 20111893 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sensory neuron-associated macrophages as novel modulators of neuropathic pain.Pain Rep. 2021 Mar 9;6(1):e873. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000000873. eCollection 2021. Pain Rep. 2021. PMID: 33981924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glia and pain: is chronic pain a gliopathy?Pain. 2013 Dec;154 Suppl 1(0 1):S10-S28. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.06.022. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Pain. 2013. PMID: 23792284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CB2 receptor deletion on myeloid cells enhanced mechanical allodynia in a mouse model of neuropathic pain.Sci Rep. 2019 May 16;9(1):7468. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43858-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31097758 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-3 (MKP-3) is necessary for the normal resolution of mechanical allodynia in a mouse model of acute postoperative pain.J Neurosci. 2013 Oct 23;33(43):17182-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5605-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24155322 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid CB(2) receptors modulate ERK-1/2 kinase signalling and NO release in microglial cells stimulated with bacterial lipopolysaccharide.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;165(6):1773-1788. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01673.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. Retraction in: Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Aug;174(15):2609. doi: 10.1111/bph.13915 PMID: 21951063 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Romero-Sandoval EA, Nutile-McMenemy N, DeLeo JA. Microglia Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 Activation Reduces Cytokine and Nitric Oxide Production by Modulating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Phosphatase (MKP) and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) 17th Neuropharmacology Conference, Cannabinoid Signaling in the Nervous System, October 31st – November 2nd, San Diego, USA. 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

