Gene discovery using massively parallel pyrosequencing to develop ESTs for the flesh fly Sarcophaga crassipalpis
- PMID: 19454017
- PMCID: PMC2700817
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-234
Gene discovery using massively parallel pyrosequencing to develop ESTs for the flesh fly Sarcophaga crassipalpis
Abstract
Background: Flesh flies in the genus Sarcophaga are important models for investigating endocrinology, diapause, cold hardiness, reproduction, and immunity. Despite the prominence of Sarcophaga flesh flies as models for insect physiology and biochemistry, and in forensic studies, little genomic or transcriptomic data are available for members of this genus. We used massively parallel pyrosequencing on the Roche 454-FLX platform to produce a substantial EST dataset for the flesh fly Sarcophaga crassipalpis. To maximize sequence diversity, we pooled RNA extracted from whole bodies of all life stages and normalized the cDNA pool after reverse transcription.
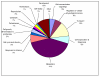
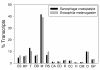
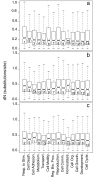
Results: We obtained 207,110 ESTs with an average read length of 241 bp. These reads assembled into 20,995 contigs and 31,056 singletons. Using BLAST searches of the NR and NT databases we were able to identify 11,757 unique gene elements (E<0.0001) representing approximately 9,000 independent transcripts. Comparison of the distribution of S. crassipalpis unigenes among GO Biological Process functional groups with that of the Drosophila melanogaster transcriptome suggests that our ESTs are broadly representative of the flesh fly transcriptome. Insertion and deletion errors in 454 sequencing present a serious hurdle to comparative transcriptome analysis. Aided by a new approach to correcting for these errors, we performed a comparative analysis of genetic divergence across GO categories among S. crassipalpis, D. melanogaster, and Anopheles gambiae. The results suggest that non-synonymous substitutions occur at similar rates across categories, although genes related to response to stimuli may evolve slightly faster. In addition, we identified over 500 potential microsatellite loci and more than 12,000 SNPs among our ESTs.
Conclusion: Our data provides the first large-scale EST-project for flesh flies, a much-needed resource for exploring this model species. In addition, we identified a large number of potential microsatellite and SNP markers that could be used in population and systematic studies of S. crassipalpis and other flesh flies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sympatric ecological speciation meets pyrosequencing: sampling the transcriptome of the apple maggot Rhagoletis pomonella.BMC Genomics. 2009 Dec 27;10:633. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-633. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 20035631 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of the housefly (Musca domestica) larva using massively parallel pyrosequencing.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Feb;39(2):1927-34. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-0939-3. Epub 2011 Jun 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 21643958
-
Identification and analysis of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) transcriptomes by massively parallel pyrosequencing.BMC Plant Biol. 2011 Oct 11;11:135. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-135. BMC Plant Biol. 2011. PMID: 21985325 Free PMC article.
-
Massively parallel pyrosequencing-based transcriptome analyses of small brown planthopper (Laodelphax striatellus), a vector insect transmitting rice stripe virus (RSV).BMC Genomics. 2010 May 13;11:303. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-303. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20462456 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of 454-ESTs from Huperzia serrata and Phlegmariurus carinatus reveals putative genes involved in lycopodium alkaloid biosynthesis and developmental regulation.BMC Plant Biol. 2010 Sep 21;10:209. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-209. BMC Plant Biol. 2010. PMID: 20854695 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gene expression, metabolic regulation and stress tolerance during diapause.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Jul;67(14):2405-24. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0311-0. Epub 2010 Mar 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20213274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome analysis of Bupleurum chinense focusing on genes involved in the biosynthesis of saikosaponins.BMC Genomics. 2011 Nov 2;12:539. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-539. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22047182 Free PMC article.
-
Deep sequencing of New World screw-worm transcripts to discover genes involved in insecticide resistance.BMC Genomics. 2010 Dec 8;11:695. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-695. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21143848 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. by Illumina paired-end RNA sequencing and SSR marker discovery.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 2;9(1):e84105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084105. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24392108 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between Normalised and Unnormalised 454-Sequencing Libraries for Small-Scale RNA-Seq Studies.Comp Funct Genomics. 2012;2012:281693. doi: 10.1155/2012/281693. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Comp Funct Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22319409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fraenkel G, Sivasubramanian P, Zdarek J. Hormonal factors in CNS and hemolymph of pupariating fly larvae which accelerate puparium formation and tanning. Biol Bull. 1972;143:127–139. doi: 10.2307/1540333. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

