Essential role of KLF5 transcription factor in cell proliferation and differentiation and its implications for human diseases
- PMID: 19448973
- PMCID: PMC11115749
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0045-z
Essential role of KLF5 transcription factor in cell proliferation and differentiation and its implications for human diseases
Abstract
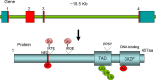
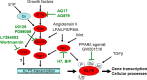
KLF5 (Kruppel-like factor 5) is a basic transcription factor binding to GC boxes at a number of gene promoters and regulating their transcription. KLF5 is expressed during development and, in adults, with higher levels in proliferating epithelial cells. The expression and activity of KLF5 are regulated by multiple signaling pathways, including Ras/MAPK, PKC, and TGFbeta, and various posttranslational modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and sumoylation. Consistently, KLF5 mediates the signaling functions in cell proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, migration, differentiation, and stemness by regulating gene expression in response to environment stimuli. The expression of KLF5 is frequently abnormal in human cancers and in cardiovascular disease-associated vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Due to its significant functions in cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation, KLF5 could be a potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The roles and regulation of the KLF5 transcription factor in cancers.Cancer Sci. 2021 Jun;112(6):2097-2117. doi: 10.1111/cas.14910. Epub 2021 May 3. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33811715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ras inhibits TGF-β-induced KLF5 acetylation and transcriptional complex assembly via regulating SMAD2/3 phosphorylation in epithelial cells.J Cell Biochem. 2020 Mar;121(3):2197-2208. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29443. Epub 2019 Nov 13. J Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31724223
-
Pro-proliferative factor KLF5 becomes anti-proliferative in epithelial homeostasis upon signaling-mediated modification.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 6;284(10):6071-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806270200. Epub 2008 Dec 4. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19056724 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Krüppel-like factor 5 in kidney disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Mar;25(5):2342-2355. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16332. Epub 2021 Feb 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33523554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different expression patterns and functions of acetylated and unacetylated Klf5 in the proliferation and differentiation of prostatic epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 5;8(6):e65538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065538. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23755247 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Restoring KLF5 in esophageal squamous cell cancer cells activates the JNK pathway leading to apoptosis and reduced cell survival.Neoplasia. 2013 May;15(5):472-80. doi: 10.1593/neo.122126. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 23633919 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation of KLF5 maintains EMT and tumorigenicity to cause chemoresistant bone metastasis in prostate cancer.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 17;12(1):1714. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21976-w. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33731701 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Glycation End Products Increase MDM2 Expression via Transcription Factor KLF5.J Diabetes Res. 2018 Sep 9;2018:3274084. doi: 10.1155/2018/3274084. eCollection 2018. J Diabetes Res. 2018. PMID: 30271790 Free PMC article.
-
KLF5 promotes the tumorigenesis and metastatic potential of thyroid cancer cells through the NF-κB signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2018 Nov;40(5):2608-2618. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6687. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30226614 Free PMC article.
-
WW Domain-Containing E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 1: A Self-Disciplined Oncoprotein.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 12;9:757493. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.757493. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34712671 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

