RAG-1 and ATM coordinate monoallelic recombination and nuclear positioning of immunoglobulin loci
- PMID: 19448632
- PMCID: PMC2693356
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1735
RAG-1 and ATM coordinate monoallelic recombination and nuclear positioning of immunoglobulin loci
Erratum in
- Nat Immunol. 2009 Jun;10(6). doi: 10.1038/ni.1735
- Nat Immunol. 2009 Sep;10(9):1034
- Nat Immunol. 2010 Mar;11(4):355-6
Abstract
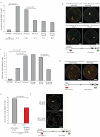
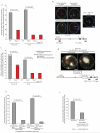
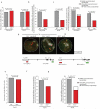
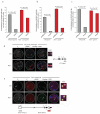
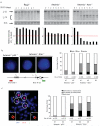
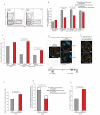
Coordinated recombination of homologous antigen receptor loci is thought to be important for allelic exclusion. Here we show that homologous immunoglobulin alleles pair in a stage-specific way that mirrors the recombination patterns of these loci. The frequency of homologous immunoglobulin pairing was much lower in the absence of the RAG-1-RAG-2 recombinase and was restored in Rag1-/- developing B cells with a transgene expressing a RAG-1 active-site mutant that supported DNA binding but not cleavage. The introduction of DNA breaks on one immunoglobulin allele induced ATM-dependent repositioning of the other allele to pericentromeric heterochromatin. ATM activated by the cleaved allele acts in trans on the uncleaved allele to prevent biallelic recombination and chromosome breaks or translocations.
Figures
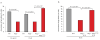

Similar articles
-
It takes two: communication between homologous alleles preserves genomic stability during V(D)J recombination.Nucleus. 2010 Jan-Feb;1(1):23-9. doi: 10.4161/nucl.1.1.10595. Nucleus. 2010. PMID: 21327101 Free PMC article.
-
The ataxia telangiectasia mutated kinase controls Igκ allelic exclusion by inhibiting secondary Vκ-to-Jκ rearrangements.J Exp Med. 2013 Feb 11;210(2):233-9. doi: 10.1084/jem.20121605. Epub 2013 Feb 4. J Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23382544 Free PMC article.
-
Nemo-Dependent, ATM-Mediated Signals from RAG DNA Breaks at Igk Feedback Inhibit V κ Recombination to Enforce Igκ Allelic Exclusion.J Immunol. 2022 Jan 15;208(2):371-383. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100696. Epub 2021 Dec 29. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34965965 Free PMC article.
-
ATM prevents unattended DNA double strand breaks on site and in generations to come.Cancer Biol Ther. 2007 Dec;6(12):1837-9. doi: 10.4161/cbt.6.12.5336. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007. PMID: 18087222 Review.
-
Breaking down cell cycle checkpoints and DNA repair during antigen receptor gene assembly.Oncogene. 2007 Dec 10;26(56):7759-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210873. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 18066088 Review.
Cited by
-
The RAG2 C-terminus and ATM protect genome integrity by controlling antigen receptor gene cleavage.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2231. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3231. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23900513 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic aspects of lymphocyte antigen receptor gene rearrangement or 'when stochasticity completes randomness'.Immunology. 2013 Jun;139(2):141-50. doi: 10.1111/imm.12057. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23278765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Igκ gene enhancers, E3' and Ed, are essential for triggering transcription.J Immunol. 2010 Dec 15;185(12):7544-52. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002665. Epub 2010 Nov 12. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21076060 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics of haematopoietic cell development.Nat Rev Immunol. 2011 Jun 10;11(7):478-88. doi: 10.1038/nri2991. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21660052 Review.
-
β-Catenin induces T-cell transformation by promoting genomic instability.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 7;111(1):391-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315752111. Epub 2013 Dec 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24371308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hesslein DG, Schatz DG. Factors and forces controlling V(D)J recombination. Adv Immunol. 2001;78:169–232. - PubMed
-
- Bassing CH, Swat W, Alt FW. The mechanism and regulation of chromosomal V(D)J recombination. Cell. 2002;109(Suppl):S45–55. - PubMed
-
- Hsu LY, et al. A conserved transcriptional enhancer regulates RAG gene expression in developing B cells. Immunity. 2003;19:105–17. - PubMed
-
- Gellert M. V(D)J recombination: RAG proteins, repair factors, and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:101–32. - PubMed
-
- Roth DB. Restraining the V(D)J recombinase. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:656–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

