Protein-protein interaction based on pairwise similarity
- PMID: 19445721
- PMCID: PMC2701420
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-150
Protein-protein interaction based on pairwise similarity
Abstract
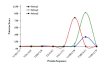
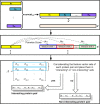
Background: Protein-protein interaction (PPI) is essential to most biological processes. Abnormal interactions may have implications in a number of neurological syndromes. Given that the association and dissociation of protein molecules is crucial, computational tools capable of effectively identifying PPI are desirable. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective method to detect PPI based on pairwise similarity and using only the primary structure of the protein. The PPI based on Pairwise Similarity (PPI-PS) method consists of a representation of each protein sequence by a vector of pairwise similarities against large subsequences of amino acids created by a shifting window which passes over concatenated protein training sequences. Each coordinate of this vector is typically the E-value of the Smith-Waterman score. These vectors are then used to compute the kernel matrix which will be exploited in conjunction with support vector machines.
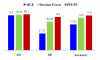
Results: To assess the ability of the proposed method to recognize the difference between "interacted" and "non-interacted" proteins pairs, we applied it on different datasets from the available yeast saccharomyces cerevisiae protein interaction. The proposed method achieved reasonable improvement over the existing state-of-the-art methods for PPI prediction.
Conclusion: Pairwise similarity score provides a relevant measure of similarity between protein sequences. This similarity incorporates biological knowledge about proteins and it is extremely powerful when combined with support vector machine to predict PPI.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RVMAB: Using the Relevance Vector Machine Model Combined with Average Blocks to Predict the Interactions of Proteins from Protein Sequences.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 18;17(5):757. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050757. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27213337 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative assessment of the structural bias in protein-protein interaction assays.Proteomics. 2008 Nov;8(22):4657-67. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200800150. Proteomics. 2008. PMID: 18924110
-
Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions via Random Ferns with Evolutionary Matrix Representation.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Feb 22;2022:7191684. doi: 10.1155/2022/7191684. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 35242211 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting domain-domain interaction based on domain profiles with feature selection and support vector machines.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Oct 29;11:537. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-537. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 21034480 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions from the Molecular to the Proteome Level.Chem Rev. 2016 Apr 27;116(8):4884-909. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00683. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Chem Rev. 2016. PMID: 27074302 Review.
Cited by
-
Improving protein function prediction using protein sequence and GO-term similarities.Bioinformatics. 2019 Apr 1;35(7):1116-1124. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty751. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30169569 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of self-interacting proteins by exploring evolutionary information embedded in PSI-BLAST-constructed position specific scoring matrix.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):82440-82449. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12517. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27732957 Free PMC article.
-
An expert rule-based approach for identifying infantile-onset Pompe disease patients using retrospective electronic health records.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 14;14(1):21523. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72259-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39277702 Free PMC article.
-
Functional classification of proteins based on projection of amino acid sequences: application for prediction of protein kinase substrates.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Jun 10;11:313. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-313. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20537135 Free PMC article.
-
Fundamentals of protein interaction network mapping.Mol Syst Biol. 2015 Dec 17;11(12):848. doi: 10.15252/msb.20156351. Mol Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 26681426 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sprinzak E, Margalit H. Correlated sequence-signatures as markers of protein-protein interaction. J Mol Biol. 2001;311:681–692. - PubMed
-
- Bartel PL, Fields S. The yeast two-hybrid system In Advances in Molecular Biology. Oxford University Press; 1997.
-
- Gavin AC, Bösche M, Krause R, Grandi P, Marzioch M, Bauer A, Schultz J, Rick J, Michon AM, Cruciat CM. Functional organization of the yeast proteome by systematic analysis of protein complexes. Nature. 2002;415:141–147. - PubMed
-
- Rigaut G, Shevchenko A, Rutz B, Wilm M, Mann M, Seraphin B. A generic protein purification method for protein complex characterization and proteome exploration. Nature Biotechnology. 1999;17:1030–1032. - PubMed
-
- Heng Z, Metin B, Rhonda B, David H, Antonic C, Paul B, Ning L, Ronald J, Scott B, Thomas H. Global analysis of protein activities using proteome chips. Science. 2001;293:2101–2105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

