Genome-wide massively parallel sequencing of formaldehyde fixed-paraffin embedded (FFPE) tumor tissues for copy-number- and mutation-analysis
- PMID: 19440246
- PMCID: PMC2678265
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005548
Genome-wide massively parallel sequencing of formaldehyde fixed-paraffin embedded (FFPE) tumor tissues for copy-number- and mutation-analysis
Abstract
Background: Cancer re-sequencing programs rely on DNA isolated from fresh snap frozen tissues, the preparation of which is combined with additional preservation efforts. Tissue samples at pathology departments are routinely stored as formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples and their use would open up access to a variety of clinical trials. However, FFPE preparation is incompatible with many down-stream molecular biology techniques such as PCR based amplification methods and gene expression studies.
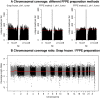
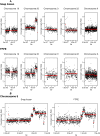
Methodology/principal findings: Here we investigated the sample quality requirements of FFPE tissues for massively parallel short-read sequencing approaches. We evaluated key variables of pre-fixation, fixation related and post-fixation processes that occur in routine medical service (e.g. degree of autolysis, duration of fixation and of storage). We also investigated the influence of tissue storage time on sequencing quality by using material that was up to 18 years old. Finally, we analyzed normal and tumor breast tissues using the Sequencing by Synthesis technique (Illumina Genome Analyzer, Solexa) to simultaneously localize genome-wide copy number alterations and to detect genomic variations such as substitutions and point-deletions and/or insertions in FFPE tissue samples.
Conclusions/significance: The application of second generation sequencing techniques on small amounts of FFPE material opens up the possibility to analyze tissue samples which have been collected during routine clinical work as well as in the context of clinical trials. This is in particular important since FFPE samples are amply available from surgical tumor resections and histopathological diagnosis, and comprise tissue from precursor lesions, primary tumors, lymphogenic and/or hematogenic metastases. Large-scale studies using this tissue material will result in a better prediction of the prognosis of cancer patients and the early identification of patients which will respond to therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
[High-throughput sequencing of frozen and paraffin-embedded tumor and normal tissue].Pathologe. 2010 Oct;31 Suppl 2:255-7. doi: 10.1007/s00292-010-1377-z. Pathologe. 2010. PMID: 20812012 German.
-
Comparison of pre-analytical FFPE sample preparation methods and their impact on massively parallel sequencing in routine diagnostics.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 8;9(8):e104566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104566. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25105902 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted high throughput sequencing in clinical cancer settings: formaldehyde fixed-paraffin embedded (FFPE) tumor tissues, input amount and tumor heterogeneity.BMC Med Genomics. 2011 Sep 29;4:68. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-4-68. BMC Med Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21958464 Free PMC article.
-
A critical spotlight on the paradigms of FFPE-DNA sequencing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Aug 11;51(14):7143-7162. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad519. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37351572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of alpha human papillomaviruses in archival formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue specimens.J Clin Virol. 2016 Mar;76 Suppl 1:S88-S97. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2015.10.007. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Clin Virol. 2016. PMID: 26514313 Review.
Cited by
-
Effective DNA/RNA co-extraction for analysis of microRNAs, mRNAs, and genomic DNA from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded specimens.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034683. Epub 2012 Apr 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22514653 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing Ventana chromogenic dual in-situ hybridization for mucinous epithelial ovarian cancer.BMC Res Notes. 2013 Dec 28;6:562. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-562. BMC Res Notes. 2013. PMID: 24373486 Free PMC article.
-
Obstacles to precision oncology: confronting current factors affecting the successful introduction of biomarkers to the clinic.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2015 Feb;38(1):39-48. doi: 10.1007/s13402-014-0192-6. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2015. PMID: 25185990 Review.
-
Identification of high-confidence somatic mutations in whole genome sequence of formalin-fixed breast cancer specimens.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Aug;40(14):e107. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks299. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22492626 Free PMC article.
-
Robustness of Next Generation Sequencing on Older Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 29;10(7):e0127353. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127353. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26222067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shendure J, Ji H. Next-generation DNA sequencing. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:1135–1145. - PubMed
-
- Velculescu VE, Kinzler KW. Gene expression analysis goes digital. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:878–880. - PubMed
-
- Sultan M, Schulz MH, Richard H, Magen A, Klingenhoff A, et al. A global view of gene activity and alternative splicing by deep sequencing of the human transcriptome. Science. 2008;321:956–960. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

