Conserved waters mediate structural and functional activation of family A (rhodopsin-like) G protein-coupled receptors
- PMID: 19433801
- PMCID: PMC2688986
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0903545106
Conserved waters mediate structural and functional activation of family A (rhodopsin-like) G protein-coupled receptors
Abstract
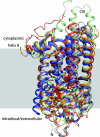
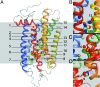
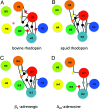
G protein-coupled receptors with seven transmembrane alpha-helices (GPCRs) comprise the largest receptor superfamily and are involved in detecting a wide variety of extracellular stimuli. The availability of high-resolution crystal structures of five prototypical GPCRs, bovine and squid rhodopsin, engineered A(2A)-adenosine, beta(1)- and beta(2)-adrenergic receptors, permits comparative analysis of features common to these and likely all GPCRs. We provide an analysis of the distribution of water molecules in the transmembrane region of these GPCR structures and find conserved contacts with microdomains demonstrated to be involved in receptor activation. Colocalization of water molecules associating with highly conserved and functionally important residues in several of these GPCR crystal structures supports the notion that these waters are likely to be as important to proper receptor function as the conserved residues. Moreover, in the absence of large conformational changes in rhodopsin after photoactivation, we propose that ordered waters contribute to the functional plasticity needed to transmit activation signals from the retinal-binding pocket to the cytoplasmic face of rhodopsin and that fundamental features of the mechanism of activation, involving these conserved waters, are shared by many if not all family A receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Agonist-induced conformational changes in bovine rhodopsin: insight into activation of G-protein-coupled receptors.J Mol Biol. 2008 Oct 3;382(2):539-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.06.084. Epub 2008 Jul 7. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18638482
-
Functional role of internal water molecules in rhodopsin revealed by X-ray crystallography.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Apr 30;99(9):5982-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.082666399. Epub 2002 Apr 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11972040 Free PMC article.
-
Relevance of rhodopsin studies for GPCR activation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 May;1837(5):674-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24041646 Review.
-
The structural basis of agonist-induced activation in constitutively active rhodopsin.Nature. 2011 Mar 31;471(7340):656-60. doi: 10.1038/nature09795. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21389983 Free PMC article.
-
Visualizing water molecules in transmembrane proteins using radiolytic labeling methods.Biochemistry. 2010 Feb 9;49(5):827-34. doi: 10.1021/bi901889t. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20047303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polar transmembrane interactions drive formation of ligand-specific and signal pathway-biased family B G protein-coupled receptor conformations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Mar 26;110(13):5211-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221585110. Epub 2013 Mar 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23479653 Free PMC article.
-
The G protein-coupled receptor rhodopsin: a historical perspective.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1271:3-18. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2330-4_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25697513 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and dynamics of protein waters revealed by radiolysis and mass spectrometry.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 11;109(37):14882-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1209060109. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22927377 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering Salt Bridge Networks between Transmembrane Helices Confers Thermostability in G-Protein-Coupled Receptors.J Chem Theory Comput. 2018 Dec 11;14(12):6574-6585. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.8b00602. Epub 2018 Nov 6. J Chem Theory Comput. 2018. PMID: 30359017 Free PMC article.
-
Photochemistry of visual pigment in a G(q) protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)--insights from structural and spectral tuning studies on squid rhodopsin.Chemistry. 2010 Feb 8;16(6):1744-9. doi: 10.1002/chem.200903194. Chemistry. 2010. PMID: 20066712 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Palczewski K, et al. Crystal structure of rhodopsin: A G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 2000;289:739–745. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Edwards PC, Burghammer M, Villa C, Schertler GF. Structure of bovine rhodopsin in a trigonal crystal form. J Mol Biol. 2004;343:1409–1438. - PubMed
-
- Okada T, et al. The retinal conformation and its environment in rhodopsin in light of a new 2.2 A crystal structure. J Mol Biol. 2004;342:571–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

