Large-scale mRNA sequencing determines global regulation of RNA editing during brain development
- PMID: 19420382
- PMCID: PMC2694479
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.089409.108
Large-scale mRNA sequencing determines global regulation of RNA editing during brain development
Abstract
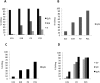
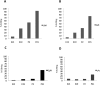
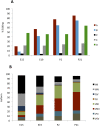
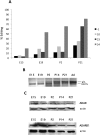
RNA editing by adenosine deamination has been shown to generate multiple isoforms of several neural receptors, often with profound effects on receptor function. However, little is known about the regulation of editing activity during development. We have developed a large-scale RNA sequencing protocol to determine adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) editing frequencies in the coding region of genes in the mammalian brain. Using the 454 Life Sciences (Roche) Amplicon Sequencing technology, we were able to determine even low levels of editing with high accuracy. The efficiency of editing for 28 different sites was analyzed during the development of the mouse brain from embryogenesis to adulthood. We show that, with few exceptions, the editing efficiency is low during embryogenesis, increasing gradually at different rates up to the adult mouse. The variation in editing gave receptors like HTR2C and GABA(A) (gamma-aminobutyric acid type A) a different set of protein isoforms during development from those in the adult animal. Furthermore, we show that this regulation of editing activity cannot be explained by an altered expression of the ADAR proteins but, rather, by the presence of a regulatory network that controls the editing activity during development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global regulation of alternative splicing by adenosine deaminase acting on RNA (ADAR).RNA. 2013 May;19(5):591-604. doi: 10.1261/rna.038042.112. Epub 2013 Mar 8. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23474544 Free PMC article.
-
A-to-I RNA editing in the rat brain is age-dependent, region-specific and sensitive to environmental stress across generations.BMC Genomics. 2018 Jan 8;19(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4409-8. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29310578 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of phospholipase C activation and alternative ADAR1 and ADAR2 pre-mRNA splicing in modulating serotonin 2C-receptor editing in vivo.RNA. 2010 Sep;16(9):1779-85. doi: 10.1261/rna.2188110. Epub 2010 Jul 22. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20651031 Free PMC article.
-
Using mouse models to unlock the secrets of non-synonymous RNA editing.Methods. 2019 Mar 1;156:40-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.10.016. Epub 2018 Oct 26. Methods. 2019. PMID: 30827465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In cancer, A-to-I RNA editing can be the driver, the passenger, or the mechanic.Drug Resist Updat. 2017 May;32:16-22. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2017.09.001. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Drug Resist Updat. 2017. PMID: 29145975 Review.
Cited by
-
Sexually dimorphic characteristics of dopamine D1 receptor-expressing neurons within the shell of the nucleus accumbens of adolescent mice.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 16:rs.3.rs-3717874. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3717874/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Biol Sex Differ. 2024 Jul 13;15(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13293-024-00631-1. PMID: 38168228 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Comprehensive analysis of RNA-Seq data reveals extensive RNA editing in a human transcriptome.Nat Biotechnol. 2012 Feb 12;30(3):253-60. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2122. Nat Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22327324
-
Single-nucleotide variants in human RNA: RNA editing and beyond.Brief Funct Genomics. 2019 Feb 14;18(1):30-39. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/ely032. Brief Funct Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30312373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABAA Receptor Subunit α3 in Network Dynamics in the Medial Entorhinal Cortex.Front Syst Neurosci. 2019 Mar 15;13:10. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2019.00010. eCollection 2019. Front Syst Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30930755 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish Adar2 Edits the Q/R site of AMPA receptor Subunit gria2α transcript to ensure normal development of nervous system and cranial neural crest cells.PLoS One. 2014 May 12;9(5):e97133. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097133. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24818983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernard A., Khrestchatisky M. Assessing the extent of RNA editing in the TMII regions of GluR5 and GluR6 kainate receptors during rat brain development. J. Neurochem. 1994;62:2057–2060. - PubMed
-
- Bernard A., Ferhat L., Dessi F., Charton G., Represa A., Ben-Ari Y., Khrestchatisky M. Q/R editing of the rat GluR5 and GluR6 kainate receptors in vivo and in vitro: Evidence for independent developmental, pathological and cellular regulation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999;11:604–616. - PubMed
-
- Bhalla T., Rosenthal J.J., Holmgren M., Reenan R. Control of human potassium channel inactivation by editing of a small mRNA hairpin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004;11:950–956. - PubMed
-
- Brusa R., Zimmermann F., Koh D.S., Feldmeyer D., Gass P., Seeburg P.H., Sprengel R. Early-onset epilepsy and postnatal lethality associated with an editing-deficient GluR-B allele in mice. Science. 1995;270:1677–1680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
