X-box binding protein 1 contributes to induction of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic cycle under hypoxic conditions
- PMID: 19403667
- PMCID: PMC2704782
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00076-09
X-box binding protein 1 contributes to induction of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic cycle under hypoxic conditions
Abstract
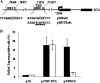
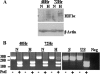
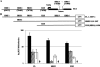
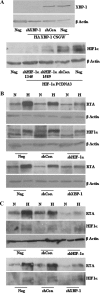
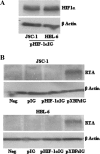
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), like other herpesviruses, has two stages to its life cycle: latency and lytic replication. KSHV is required for development of Kaposi's sarcoma, a tumor of endothelial origin, and is associated with the B-cell tumor primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) and the plasmablastic variant of multicentric Castleman's disease, all of which are characterized by predominantly latent KSHV infection. Recently, we and others have shown that the activated form of transcription factor X-box binding protein 1 (XBP-1) is a physiological trigger of KSHV lytic reactivation in PEL. Here, we show that XBP-1s transactivates the ORF50/RTA promoter though an ACGT core containing the XBP-1 response element, an element previously identified as a weakly active hypoxia response element (HRE). Hypoxia induces the KSHV lytic cycle, and active HREs that respond to hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha are present in the ORF50/RTA promoter. Hypoxia also induces active XBP-1s, and here, we show that both transcription factors contribute to the induction of RTA expression, leading to the production of infectious KSHV under hypoxic conditions.
Figures
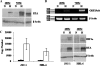
Similar articles
-
Induction of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded Thymidine Kinase (ORF21) by X-Box Binding Protein 1.J Virol. 2020 Feb 14;94(5):e01555-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01555-19. Print 2020 Feb 14. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31801863 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded Viral Interleukin-6 by X-Box Binding Protein 1.J Virol. 2015 Oct 21;90(1):368-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01192-15. Print 2016 Jan 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26491160 Free PMC article.
-
X box binding protein XBP-1s transactivates the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) ORF50 promoter, linking plasma cell differentiation to KSHV reactivation from latency.J Virol. 2007 Dec;81(24):13578-86. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01663-07. Epub 2007 Oct 10. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17928342 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of KSHV Latency and Lytic Reactivation.Viruses. 2020 Sep 17;12(9):1034. doi: 10.3390/v12091034. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32957532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Rta/Orf50 transactivator proteins of the gamma-herpesviridae.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;312:71-100. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-34344-8_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17089794 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune evasion by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.Future Microbiol. 2010 Sep;5(9):1349-65. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.105. Future Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20860481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded Thymidine Kinase (ORF21) by X-Box Binding Protein 1.J Virol. 2020 Feb 14;94(5):e01555-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01555-19. Print 2020 Feb 14. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31801863 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency and Reactivation.Adv Virol. 2011;2011:193860. doi: 10.1155/2011/193860. Adv Virol. 2011. PMID: 21625290 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded Viral Interleukin-6 by X-Box Binding Protein 1.J Virol. 2015 Oct 21;90(1):368-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01192-15. Print 2016 Jan 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26491160 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV activates unfolded protein response sensors but suppresses downstream transcriptional responses to support lytic replication.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Dec 2;15(12):e1008185. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008185. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31790507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acosta-Alvear, D., Y. Zhou, A. Blais, M. Tsikitis, N. H. Lents, C. Arias, C. J. Lennon, Y. Kluger, and B. D. Dynlacht. 2007. XBP1 controls diverse cell type- and condition-specific transcriptional regulatory networks. Mol. Cell 2753-66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

